-
![]() The two colors visible at a splice. Credit: EYE Film Institute Amsterdam. Film: [Kleurenpracht].
The two colors visible at a splice. Credit: EYE Film Institute Amsterdam. Film: [Kleurenpracht].
- Credit: George Eastman House. Preserved by Carole Fodor, Haghefilm Digitaal fellow and graduate of The L. Jeffrey Selznick School of Film Preservation. Film: A Day with John Burroughs (Prizma, 1919).
- Credit: George Eastman House. Preserved by Carole Fodor, Haghefilm Digitaal fellow and graduate of The L. Jeffrey Selznick School of Film Preservation. Film: A Day with John Burroughs (Prizma, 1919).
- Credit: George Eastman House Motion Picture Department Collection. Film: The Land of the Great Spirit (1919).
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Orange.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Orange.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Orange.
Category: Double-coated / bi-pack▼×
- All Categories
- Bibliography
- Chromogenic monopack
- Chromolytic multilayer
- Color separation
- Edge Codes and Identification
- Hand coloring
- Other
- Printing / dye-transfer
- Printing / pigment process
- Screen processes
- Spatial synthesis (multiple lenses, beam splitter)
- Stencil coloring (pochoir, Pathécolor)
- Temporal synthesis (rotary filters)
- Theory
- Tinting
- Toning
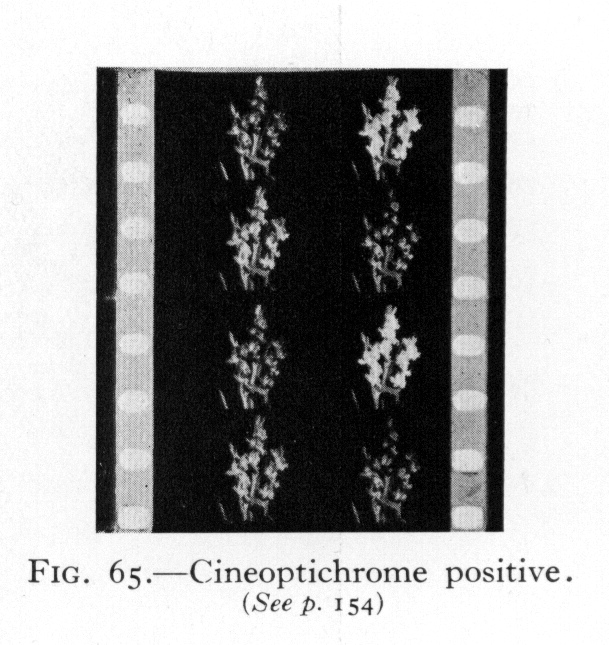
“In its final form Prizma made use of duplitized positive film. As in previous Prizma systems, the original negatives were alternate frame sequential exposures. The Prizma negative was printed on both sides of the positive film in a special ...
-
![]() Credit: Harvard Film Archive, George Huizinga Collection, item no. 10454. Film: Prehistoric Women (1951).
Credit: Harvard Film Archive, George Huizinga Collection, item no. 10454. Film: Prehistoric Women (1951).
- Credit: Harvard Film Archive, George Huizinga Collection, item no. 10454. Film: Prehistoric Women (1951).
- Source: Coe, Brian (1981): The History of Movie Photography. Westfield, N.J.: Eastview Editions.
- Reflection on Cinecolor print. Credit: Image courtesy of the 20th Century Fox Collection at the Academy Film Archive. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger
- Reflection on Cinecolor 16 mm print. Credit: Library of Congress. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger
93 Images in 9 Galleries
-
![]() Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
- Source: Coe, Brian (1981): The History of Movie Photography. Westfield, N.J.: Eastview Editions.
- Credit: Collection Gert Koshofer, Bergisch Gladbach (Germany).
16 Images in 1 Gallery
“R. Berthon and M. Audibert patented a method of obtaining a virtual image by means of an anterior lens and prisms or mirrors. This idea was further improved upon in E.P. 17,023, 1913. In F.P. 458,040 Audibert proposed to use a negative front lens ...
-
![]() Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
- Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
2 Images
-
![]() Source: Cornwell-Clyne, Adrian (1951): Colour Cinematography. London: Chapman & Hall.
Source: Cornwell-Clyne, Adrian (1951): Colour Cinematography. London: Chapman & Hall.
- Source: Cornwell-Clyne, Adrian (1951): Colour Cinematography. London: Chapman & Hall.
2 Images
“Two-colour additive process
Talkicolor was developed by Percy James Pearce along with Dr Anthony Bernardi who was also involved in the development of Raycol. The process was funded mainly by the author Elinor Glyn through her company Elinor ...
-
![]() Knowing Men (GB 1930, Elinor Glyn), negative. Credit: Courtesy of BFI National Archive. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
Knowing Men (GB 1930, Elinor Glyn), negative. Credit: Courtesy of BFI National Archive. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
3 Images in 1 Gallery
“The Brewster Process.
(U.S.P. 1,752,477. 1930-)
Camera. – P. D. Brewster, an American inventor, who was one of the first to apply the bipack system to colour cinematography, has a number of patents to his credit covering various cameras and ...
-
![]() Dyes of Brewster color. Credit: Brian Pritchard.
Dyes of Brewster color. Credit: Brian Pritchard.
- Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
52 Images in 1 Gallery
“Following the premises of one of William Friese-Greene’s systems, this two-colour subtractive process required that two reels of film be printed in parallel through a lens fitted with a prism that split light in two directions, through red ...
-
![]() Source: Wall, E.J. (1925): The History of Three-color Photography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
Source: Wall, E.J. (1925): The History of Three-color Photography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
1 Image
-
![]() Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. A History of Motion Picture Color Technology.
Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. A History of Motion Picture Color Technology.
- Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
2 Images
-
![]() Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
- Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
2 Images
-
![]() Screenshot from Mayorov, Nikolai (2012): Soviet Colours. Translated by Birgit Beumers. In: Studies in Russian & Soviet Cinema, 6:2, pp. 241–255. doi: 10.1386/srsc.6.2.241_1 Courtesy of Nikolai Mayorov.
Screenshot from Mayorov, Nikolai (2012): Soviet Colours. Translated by Birgit Beumers. In: Studies in Russian & Soviet Cinema, 6:2, pp. 241–255. doi: 10.1386/srsc.6.2.241_1 Courtesy of Nikolai Mayorov.
1 Image
“Harmonicoior was developed by French chemist Maurice Combes. It was first formally demonstrated in London by Harmonicoior Films Ltd, of 4 Great Winchester Street, on the 23 March 1936 at the Curzon Soho with the film Talking Hands, produced at ...
-
![]() Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
- Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
- Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
3 Images
“The Dutch Sirius Color process (1929) used a camera with a beamsplitting system behind the lens to expose a single film, the film passing through two gates at right angles to each other. The double-coated print film was dye-toned. The process ...
-
![]() Magnification, 20x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
Magnification, 20x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Magnification, 10x. Credit: Photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Magnification, 5x. Credit: Photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. In: Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Magnification of an image area. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Reflection on the Sirius film, front. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Reflection on the Sirius film, back. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
142 Images in 4 Galleries
-
![]() Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
- Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
2 Images
-
![]() Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
1 Image
“Douglass Color No. 2 (1919). The two negatives of the Douglass Color system No. 1 were printed on a positive. In this updated version of the process, rather than projecting the frames through red and green filters, both latent images were ...
-
![]() Magnification of an image area. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
Magnification of an image area. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Color chart. Credit: Guido Seeber Nachlass, Deutsche Kinemathek, Berlin. Source: Goergen, Jeanpaul (2010): Rotorange und blaugrün. Das Zweifarbenverfahren Ufacolor 1931-1940. In: Filmblatt, no. 43, pp. 77-92.
- Credit: Guido Seeber Nachlass, Deutsche Kinemathek, Berlin. Source: Goergen, Jeanpaul (2010): Rotorange und blaugrün. Das Zweifarbenverfahren Ufacolor 1931-1940. In: Filmblatt, no. 43, pp. 77-92.
- Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Credit: Bundesarchiv-Filmarchiv, photo: Marian Stefanowski. Source: Goergen, Jeanpaul (2010): Rotorange und blaugrün. Das Zweifarbenverfahren Ufacolor 1931-1940. In: Filmblatt, no. 43, pp. 77-92. Film: Bunte Tierwelt. Studien in Hagebecks Tierpark in Stellingen (1931).
- Credit: Bundesarchiv-Filmarchiv, photo: Marian Stefanowski. Source: Goergen, Jeanpaul (2010): Rotorange und blaugrün. Das Zweifarbenverfahren Ufacolor 1931-1940. In: Filmblatt, no. 43, pp. 77-92. Film: Karneval (1936).
- Credit: Bundesarchiv-Filmarchiv, photo: Jeanpaul Goergen. Source: Goergen, Jeanpaul (2010): Rotorange und blaugrün. Das Zweifarbenverfahren Ufacolor 1931-1940. In: Filmblatt, no. 43, pp. 77-92. Film: Bunte Fischwelt (1936).
- Credit: Bundesarchiv-Filmarchiv, photo: Marian Stefanowski. Source: Goergen, Jeanpaul (2010): Rotorange und blaugrün. Das Zweifarbenverfahren Ufacolor 1931-1940. In: Filmblatt, no. 43, pp. 77-92. Film: Karneval (1936).
- Credit: Deutsches Filminstitut DIF (Vicas Nachlass), photo: Jeanpaul Goergen. Source: Goergen, Jeanpaul (2010): Rotorange und blaugrün. Das Zweifarbenverfahren Ufacolor 1931-1940. In: Filmblatt, no. 43, pp. 77-92. Film: Potsdam (1934).
- Credit: Bundesarchiv-Filmarchiv, photo: Marian Stefanowski. Source: Goergen, Jeanpaul (2010): Rotorange und blaugrün. Das Zweifarbenverfahren Ufacolor 1931-1940. In: Filmblatt, no. 43, pp. 77-92. Film: Farben machen froh (1938).
- Magnification 5x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Magnification 10x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Magnification 20x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. In:Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Magnification of an image area. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. In:Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Reflection on Ufacolor film. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. In:Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- An opened splice of an Ufacolor positive shows the two colors used in the process. Credit: David Pfluger. Source: David Pfluger’s collection.
136 Images in 7 Galleries
“To offset the possible effects of poor contact between the various members of the tripack, J. H. Smith coated the emulsions directly one on top of the other, but with an insulating layer of collodion between them. In this manner there was ...
The Kodachrome process was invented in 1913 by John G. Capstaff for still photography and subsequently adapted to motion pictures. For the process two frames were advanced simultaneously, one located above the other. The light passed either through two lenses or through a beam-splitter, fitted with red and green filters. The release print was exposed through a beam-splitter whereby the alternate frames were projected onto either side of double-coated stock. After development by a usual b/w process, the film was tanned to harden the exposed areas. The soft areas were dyed red-orange and blue-green respectively.
-
![]() Two-Color Kodachrome Print (USA ca. 1925 to 1927, Anonymous). Credit: George Eastman Museum. Photographs of the Kodachrome two-color double coated stock from 1925 and 1927 by Olivia Kristina Stutz, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors.
Two-Color Kodachrome Print (USA ca. 1925 to 1927, Anonymous). Credit: George Eastman Museum. Photographs of the Kodachrome two-color double coated stock from 1925 and 1927 by Olivia Kristina Stutz, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors.
- Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. In:Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Magnification 5x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Magnification 10x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Magnification 20x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Kodachrome Two-color test from 1922, YouTube channel of the George Eastman House.
350 Images in 12 Galleries
-
![]() Source: Cornwell-Clyne, Adrian (1951): Colour Cinematography. London: Chapman & Hall.
Source: Cornwell-Clyne, Adrian (1951): Colour Cinematography. London: Chapman & Hall.
- Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Cornwell-Clyne, Adrian (1951): Colour Cinematography. London: Chapman & Hall.
- Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Cornwell-Clyne, Adrian (1951): Colour Cinematography. London: Chapman & Hall.
- Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Cornwell-Clyne, Adrian (1951): Colour Cinematography. London: Chapman & Hall.
- Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Cornwell-Clyne, Adrian (1951): Colour Cinematography. London: Chapman & Hall.
- Coote, Jack (1948): New Three-Color Camera, In: Journal of the Society of Motion Picture Engineers, vol. 50, June 1948, pp. 543-553.
- Coote, Jack (1948): New Three-Color Camera, In: Journal of the Society of Motion Picture Engineers, vol. 50, June 1948, pp. 543-553.
19 Images in 3 Galleries
“Harriscolor
In this method as in other methods of color photography, independent color value negatives are first obtained. The Harriscolor process can employ one of the following two methods: Either a camera wherein the dividing light prisms ...
-
![]() Credit: Technicolor Collection. George Eastman House Moving Image Department. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
Credit: Technicolor Collection. George Eastman House Moving Image Department. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Credit: Technicolor Collection. George Eastman House Moving Image Department. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Credit: Technicolor Collection. George Eastman House Moving Image Department. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
3 Images
-
![]() Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: Captain Calamity (1936)
Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: Captain Calamity (1936)
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: Captain Calamity (1936)
2 Images
“M. F. de Colombier appears to have been the first to suggest the application of this system to cinematography, and like so many French patents it is a little indefinite in phraseology. Three films were employed representing the same view and ...