- All Categories
- Bibliography
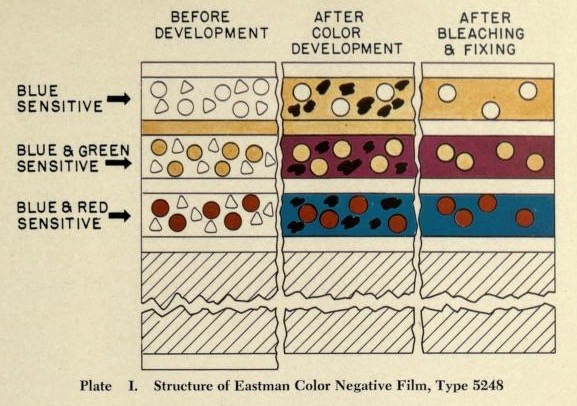
- Chromogenic monopack
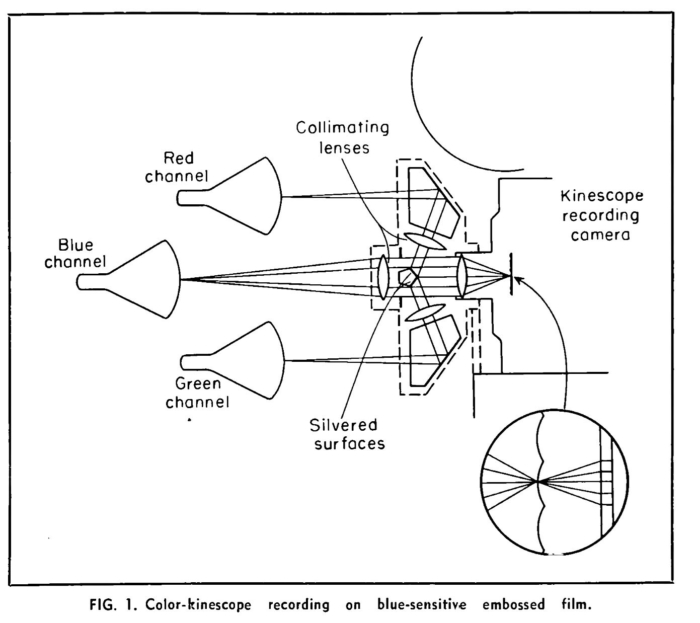
- Chromolytic multilayer
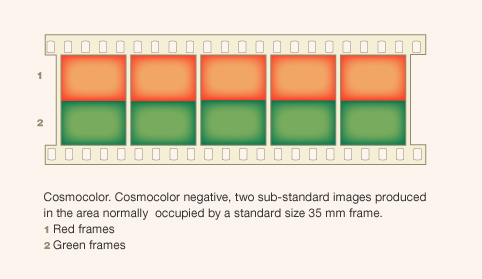
- Color separation
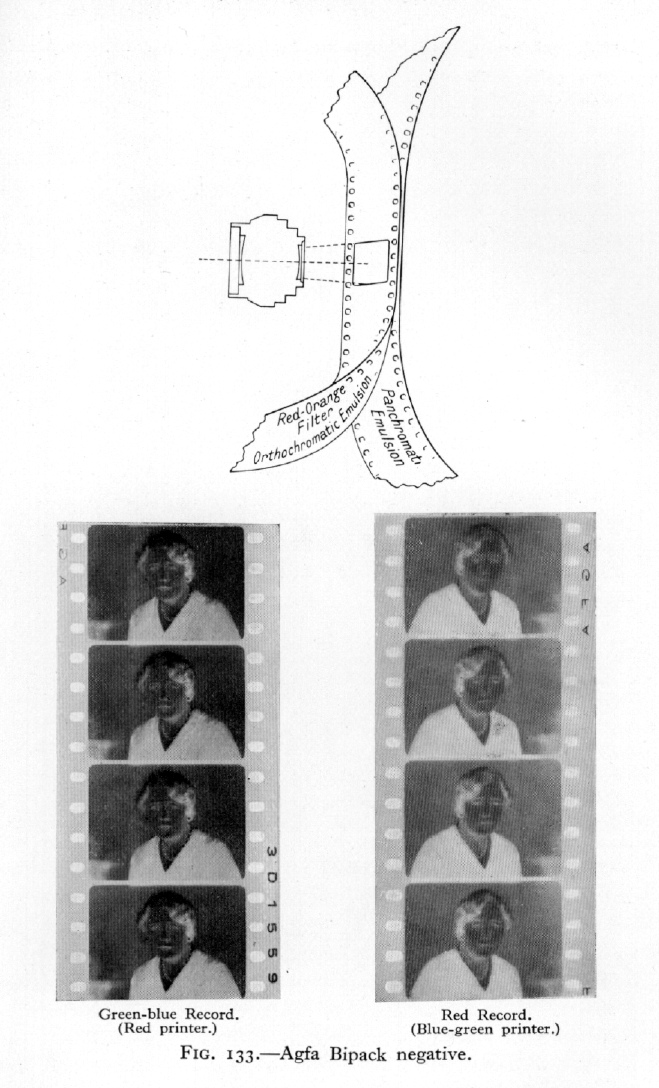
- Double-coated / bi-pack
- Edge Codes and Identification
- Hand coloring
- Other
- Printing / dye-transfer
- Printing / pigment process
- Screen processes
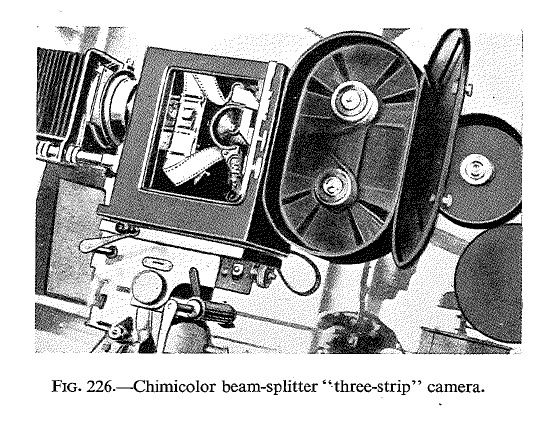
- Spatial synthesis (multiple lenses, beam splitter)
- Stencil coloring (pochoir, Pathécolor)
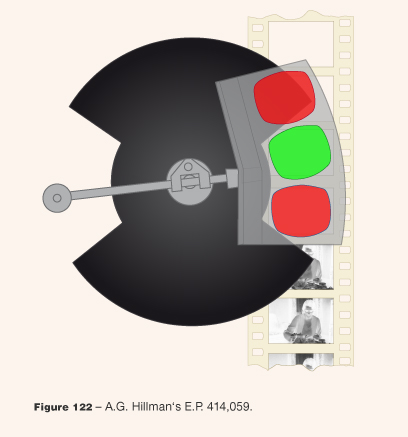
- Temporal synthesis (rotary filters)
- Theory
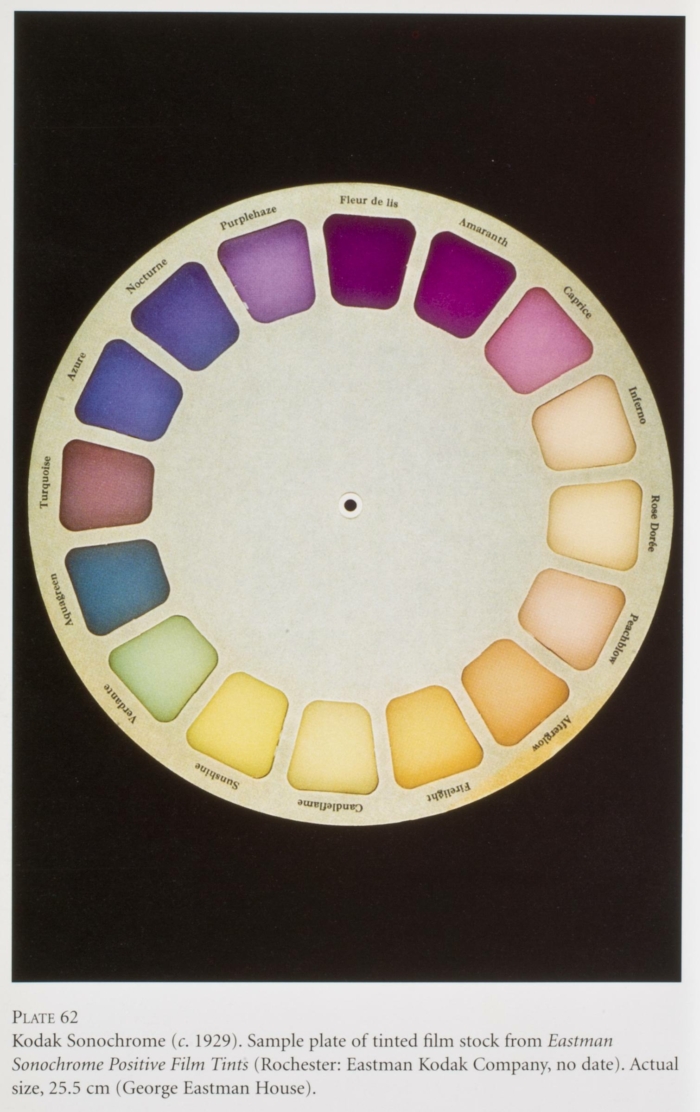
- Tinting
- Toning
-
![]() "Du Hauron invented his Chromographoscope in 1874. It could be used either as a camera or an additive viewer." Source: Coote, Jack H. (1993): The Illustrated History of Colour Photography. Surbiton, Surrey: Fountain Press.
"Du Hauron invented his Chromographoscope in 1874. It could be used either as a camera or an additive viewer." Source: Coote, Jack H. (1993): The Illustrated History of Colour Photography. Surbiton, Surrey: Fountain Press.
- An early three-color print by Louis Ducros Du Hauron, 1877.
2 Images
-
![]() „Film orthochromatique (film négatif Pathé Standard)“ (orthochromatic stock). Source: Didiée, L. (1926): Le Film vierge Pathé. Manuel de développement et de tirage. Paris: Pathé.
„Film orthochromatique (film négatif Pathé Standard)“ (orthochromatic stock). Source: Didiée, L. (1926): Le Film vierge Pathé. Manuel de développement et de tirage. Paris: Pathé.
- „Film ordinaire (non orthochromatique)“ (Normal, non-orthochromatic stock). Source: Didiée, L. (1926): Le Film vierge Pathé. Manuel de développement et de tirage. Paris: Pathé.
2 Images
-
![]() Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson.
Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson.
1 Image
-
![]() Source: Coe, Brian (1978): Colour Photography. The First Hundred Years 1840-1940. London: Ash & Grant.
Source: Coe, Brian (1978): Colour Photography. The First Hundred Years 1840-1940. London: Ash & Grant.
- Source: Lavédrine, Bertrand (2009): Photographs of the Past. Process and Preservation. Los Angeles: Getty Publications.
- Source: Coote, Jack H. (1993): The Illustrated History of Colour Photography. Surbiton, Surrey: Fountain Press.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 19.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 235.
5 Images
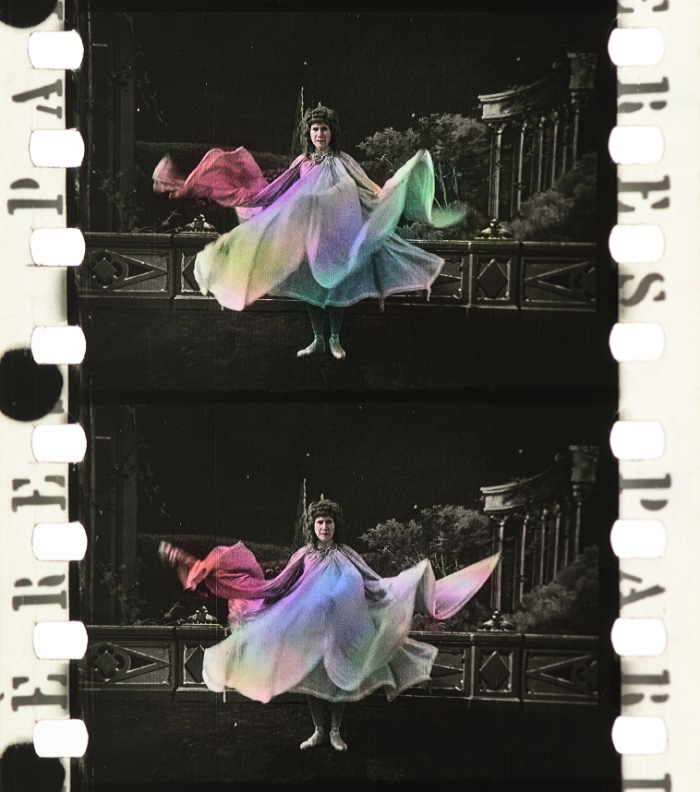
Coloring of individual frames by the use of very fine brushes. The process was previously applied to lantern slides. Any water based translucent dye was suited for the process, most often the coloring was done with acid dyes.
-
![]() Loïe Fuller (FRA 1905, Anonymous). Credit: BFI National Archive. Photographs of the hand colored nitrate print by Olivia Kristina Stutz, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors.
Loïe Fuller (FRA 1905, Anonymous). Credit: BFI National Archive. Photographs of the hand colored nitrate print by Olivia Kristina Stutz, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors.
- Métamorphoses du papillon (FRA 1904, Gaston Velle). Credit: Library of Congress. Photograph of the nitrate prints by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Credit: Turconi Collection by courtesy of George Eastman Museum, Moving Image Collection. Film: Zara.
- Credit: Paolo Cherchi Usai. Source: Cherchi Usai, Paolo (2000): Silent Cinema. London: BFI.
- Source: Coe, Brian (1981): The History of Movie Photography. Westfield, N.J.: Eastview Editions.
250 Images in 18 Galleries
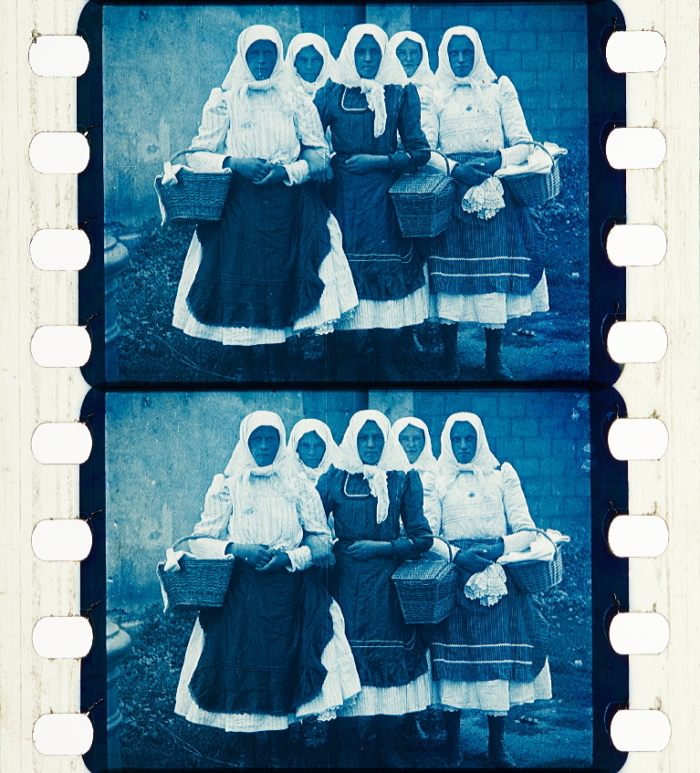
In contrast to tinting, toning is not the simple immersion of a film into a dye bath but involves a chemical reaction converting the silver image. In this reaction the neutral silver image in the emulsion of the positive film is replaced by one consisting of colored metal compounds. These were usually iron ferrocyanide (Prussian Blue) for blue, copper ferrocyanide for red/brown, silver sulfide for sepia or rarely uranium ferrocyanide for reddish brown. Toning had been used in still photography before. But since film was projected on the screen it required translucent toning compounds.
-
![]() Hongarije (FRA 1926, Anonymous). Credit: EYE Film Museum. Photographs of the tinted, toned and stencil colored nitrate print by Olivia Kristina Stutz, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors.
Hongarije (FRA 1926, Anonymous). Credit: EYE Film Museum. Photographs of the tinted, toned and stencil colored nitrate print by Olivia Kristina Stutz, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors.
- Virages sur films à support teinté Pathé, Film teinté lavande (virage bleu) lavender tinted stock with blue toning, the same image from a different copy of the book, combination of tungsten backlight with daylight toplight. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger. Source: Didiée, L. (1926): Le Film vierge Pathé. Manuel de développement et de tirage. Paris: Pathé. [quote id='16']
- Photomicrograph, 25x. Credit: Norbert Wey, Institute of Pathology, University of Zurich.
- Photomicrograph, 50x. Credit: Norbert Wey, Institute of Pathology, University of Zurich.
- Photomicrograph, 100x. Credit: Norbert Wey, Institute of Pathology, University of Zurich.
- Toning samples from the Tinting and Toning Workshop by Ulrich Ruedel, Seminar "Materiality of Film" by Barbara Flueckiger and Bregt Lameris, Department of Film Studies, University of Zurich, in collaboration with Lichtspiel / Kinemathek Bern, David Landolf and Brigitte Paulowitz.
- Toning samples from the Tinting and Toning Workshop by Ulrich Ruedel, Seminar "Materiality of Film" by Barbara Flueckiger and Bregt Lameris, Department of Film Studies, University of Zurich, in collaboration with Lichtspiel / Kinemathek Bern, David Landolf and Brigitte Paulowitz.
1549 Images in 62 Galleries
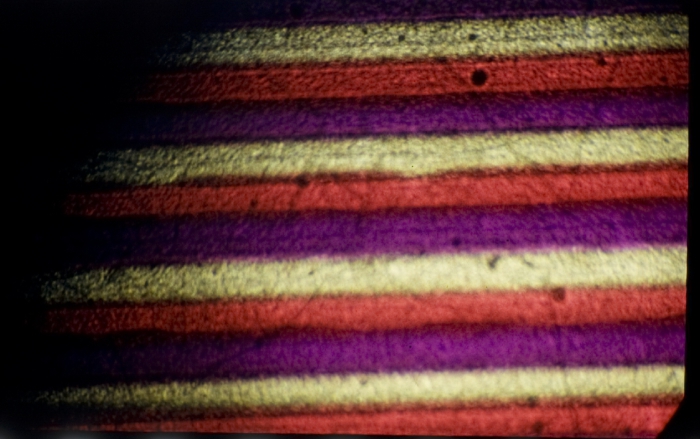
For tinting, the positive print is immersed into a variety of dye baths, scene by scene. To this end, the print has to be cut into the corresponding fragments and reassembled after the dyeing process. The dye homogeneously attaches over the entire image’s gelatin including the perforation area. Usually synthetic dyes were dissolved in a weak acid solution to form a chemical bond with the gelatin.
-
![]() Salomé (USA 1922, Charles Bryant). Credit: George Eastman Museum. Photographs of the tinted, toned and Handschiegl nitrate print by Barbara Flueckiger.
Salomé (USA 1922, Charles Bryant). Credit: George Eastman Museum. Photographs of the tinted, toned and Handschiegl nitrate print by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger. Source: Agfa Kine-Handbuch. Berlin: Actien-Gesellschaft für Anilin-Fabrikation. (around 1927, estimated).
- See Mazzanti (2009: 71). Credit: Cineteca di Bologna. Film: Lyda Borelli in Malombra (Italy, 1917).
- As coloured for South America, see Mazzanti (2009: 71). Credit: Cineteca di Bologna.
- As coloured for the domestic Italian market, see Mazzanti (2009: 71). Credit: Cineteca di Bologna.
- Photomicrograph, 25x. Credit: Norbert Wey, Institute of Pathology, University of Zurich.
- Photomicrograph, 50x. Credit: Norbert Wey, Institute of Pathology, University of Zurich.
- Photomicrograph, 50x. Credit: Norbert Wey, Institute of Pathology, University of Zurich.
- Credit: Lichtspiel / Kinemathek Bern. Film: Dagli Appennini alle Ande (ITA 1916, Umberto Paradisi). Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Credit: Lichtspiel / Kinemathek Bern. Film: Dagli Appennini alle Ande (ITA 1916, Umberto Paradisi). Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Credit: Lichtspiel / Kinemathek Bern. Film: Dagli Appennini alle Ande (ITA 1916, Umberto Paradisi). Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Credit: Lichtspiel / Kinemathek Bern. Film: Dagli Appennini alle Ande (ITA 1916, Umberto Paradisi). Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Credit: Lichtspiel / Kinemathek Bern. Film: Dagli Appennini alle Ande (ITA 1916, Umberto Paradisi). Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Credit: Lichtspiel / Kinemathek Bern. Film: Dagli Appennini alle Ande (ITA 1916, Umberto Paradisi). Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Credit: Lichtspiel / Kinemathek Bern. Film: Gaumont Woche.
- Credit: Lichtspiel / Kinemathek Bern. Film: Gaumont Woche.
- Credit: Lichtspiel / Kinemathek Bern. Film: Gaumont Woche.
- Credit: Lichtspiel / Kinemathek Bern. Film: Gaumont Woche.
- Credit: Lichtspiel / Kinemathek Bern. Film: Selznick News.
4492 Images in 111 Galleries
-
![]() Photomicrograph (20x) of a Joly screen. Credit: Courtesy of George Eastman House, International Museum of Photography and Film.
Photomicrograph (20x) of a Joly screen. Credit: Courtesy of George Eastman House, International Museum of Photography and Film.
- Credit: Courtesy of George Eastman House, International Museum of Photography and Film.
- Source: Coe, Brian (1978): Colour Photography. The First Hundred Years 1840-1940. London: Ash & Grant.
- Credit: Gawain Weaver, Photograph Conservator, Gawain Weaver Art Conservation, San Anselmo, CA.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 69.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 22.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 23.
7 Images
-
![]() Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Ede, François (1994): Jour de fête ou la couleur retrouvée. Cahiers du Cinéma: Paris.
Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Ede, François (1994): Jour de fête ou la couleur retrouvée. Cahiers du Cinéma: Paris.
- Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
- Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
- Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
4 Images
-
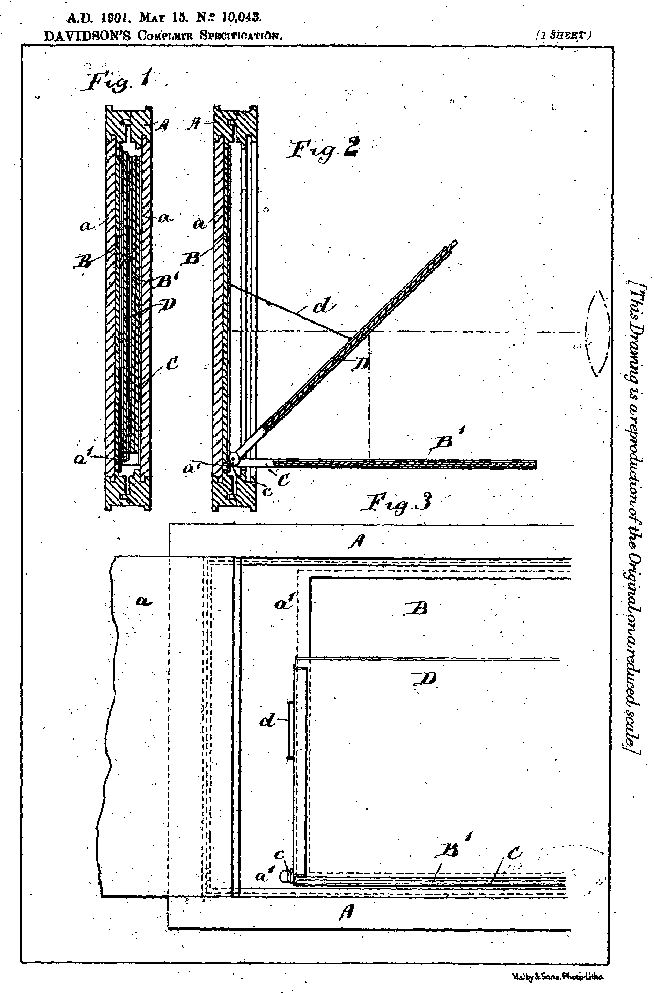
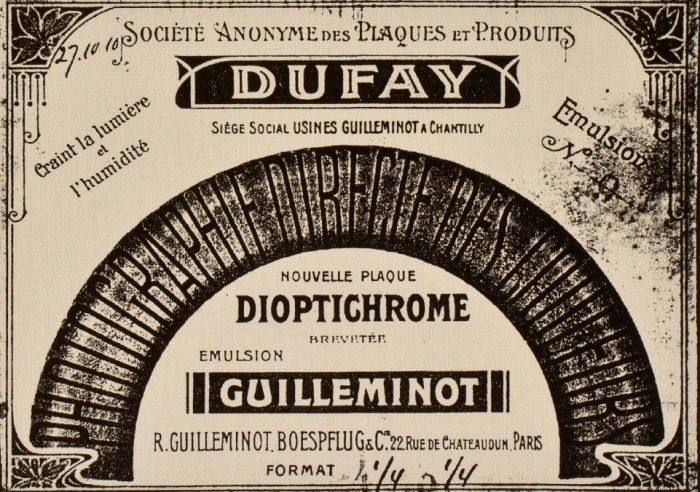
![]() Source: D.R.P. 98,799, Dec. 17, 1897
Source: D.R.P. 98,799, Dec. 17, 1897
- Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: D.R.P. 98,799, Dec. 17, 1897
2 Images
-
![]() Source: Hübl, Arthur Freiherr von (1904): Die Dreifarbenphotographie mit besonderer Berücksichtigung des Dreifarbendruckes und der photographischen Pigmentbilder in natürlichen Farben. Halle a. S.: Druck und Verlang von Wilhelm Knapp. Photograph by Martin Weiss, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors.
Source: Hübl, Arthur Freiherr von (1904): Die Dreifarbenphotographie mit besonderer Berücksichtigung des Dreifarbendruckes und der photographischen Pigmentbilder in natürlichen Farben. Halle a. S.: Druck und Verlang von Wilhelm Knapp. Photograph by Martin Weiss, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors.
- Source: Hübl, Arthur Freiherr von (1904): Die Dreifarbenphotographie mit besonderer Berücksichtigung des Dreifarbendruckes und der photographischen Pigmentbilder in natürlichen Farben. Halle a. S.: Druck und Verlang von Wilhelm Knapp. Photograph by Martin Weiss, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors.
- Source: Hübl, Arthur Freiherr von (1904): Die Dreifarbenphotographie mit besonderer Berücksichtigung des Dreifarbendruckes und der photographischen Pigmentbilder in natürlichen Farben. Halle a. S.: Druck und Verlang von Wilhelm Knapp. Photograph by Martin Weiss, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors.
- Source: Hübl, Arthur Freiherr von (1904): Die Dreifarbenphotographie mit besonderer Berücksichtigung des Dreifarbendruckes und der photographischen Pigmentbilder in natürlichen Farben. Halle a. S.: Druck und Verlang von Wilhelm Knapp. Photograph by Martin Weiss, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors.
- Source: Hübl, Arthur Freiherr von (1904): Die Dreifarbenphotographie mit besonderer Berücksichtigung des Dreifarbendruckes und der photographischen Pigmentbilder in natürlichen Farben. Halle a. S.: Druck und Verlang von Wilhelm Knapp. Photograph by Martin Weiss, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors.
- Source: Hübl, Arthur Freiherr von (1904): Die Dreifarbenphotographie mit besonderer Berücksichtigung des Dreifarbendruckes und der photographischen Pigmentbilder in natürlichen Farben. Halle a. S.: Druck und Verlang von Wilhelm Knapp. Photograph by Martin Weiss, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors.
- Source: Hübl, Arthur Freiherr von (1904): Die Dreifarbenphotographie mit besonderer Berücksichtigung des Dreifarbendruckes und der photographischen Pigmentbilder in natürlichen Farben. Halle a. S.: Druck und Verlang von Wilhelm Knapp. Photograph by Martin Weiss, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors.
- Source: Hübl, Arthur Freiherr von (1904): Die Dreifarbenphotographie mit besonderer Berücksichtigung des Dreifarbendruckes und der photographischen Pigmentbilder in natürlichen Farben. Halle a. S.: Druck und Verlang von Wilhelm Knapp. Photograph by Martin Weiss, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors.
- Source: Hübl, Arthur Freiherr von (1904): Three-Colour Photography. Three-Colour Printing and the Production of Photographic Pigment Pictures in Natural Colours. London: W.A. Penrose.
- Source: Hübl, Arthur Freiherr von (1904): Die Dreifarbenphotographie mit besonderer Berücksichtigung des Dreifarbendruckes und der photographischen Pigmentbilder in natürlichen Farben. Halle a. S.: Druck und Verlang von Wilhelm Knapp. Photograph by Martin Weiss, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors.
11 Images
“In 1898 William Friese-Greene, a professional portrait photographer by trade, demonstrated in London ‘the first process of true natural-color cinematography.’ His program consisted of ‘a series of animated natural-color pictures,’ and although this demonstration aroused considerable interest at the time, Friese-Greene was unable to exploit this system on a profitable basis. Undaunted, he eventually developed a total of four different color methods.”
-
![]() Credit: Courtesy of BFI National Archive. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger. Film: Kino the Girl of Colour (GB 1920, William Friese-Greene, Claude Friese-Greene).
Credit: Courtesy of BFI National Archive. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger. Film: Kino the Girl of Colour (GB 1920, William Friese-Greene, Claude Friese-Greene).
- Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
- Credit: Paolo Cherchi Usai. Source: Cherchi Usai, Paolo (2000): Silent Cinema. London: BFI.
112 Images in 2 Galleries
-
![]() [U-Boot]. Credit: Deutsches Filminstitut DIF. Photograph of the chromolithographic nitrate print by Barbara Flueckiger.
[U-Boot]. Credit: Deutsches Filminstitut DIF. Photograph of the chromolithographic nitrate print by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Box Der Film fürs Heimkino. Credit: Deutsches Filminstitut DIF. iPhone photo by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Box "Film for Home Cinema". Credit: Deutsches Filminstitut DIF. iPhone photo by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Box "Attention! Celluloid Film". Credit: Deutsches Filminstitut DIF. iPhone photo by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Boxes and loops. Credit: Deutsches Filminstitut DIF. iPhone photo by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Box and loops. Credit: Deutsches Filminstitut DIF. iPhone photo by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Film can for Chromolithographic Loop. Credit: Deutsches Filminstitut DIF. iPhone photo by Noemi Daugaard, SNSF Filmcolors
- Film can for Chromolithographic Loop. Credit: Deutsches Filminstitut DIF. iPhone photo by Noemi Daugaard, SNSF Filmcolors
119 Images in 3 Galleries
-
![]() „Their projector […] used three lenses and a special filter
wheel which enabled every frame of the film to be projected three times in succession through the appropriate filter as it passed through the triple frame projector aperture. Although it eventually led to the Kinemacolor two colour process, the Lee and Turner patent was not successful“. Source: Coote, Jack H. (1993): The Illustrated History of Colour Photography. Surbiton, Surrey: Fountain Press.
„Their projector […] used three lenses and a special filter
wheel which enabled every frame of the film to be projected three times in succession through the appropriate filter as it passed through the triple frame projector aperture. Although it eventually led to the Kinemacolor two colour process, the Lee and Turner patent was not successful“. Source: Coote, Jack H. (1993): The Illustrated History of Colour Photography. Surbiton, Surrey: Fountain Press.
- "The First Color Moving Pictures", from the YouTube channel of the National Media Museum. [quote id="1"]
- Lee Turner projector in the Media History Museum in Bradford.
- „In 1899 Lee and Turner obtained a patent for a three colour process of cinematography requiring a single lens camera […] making a recurring sequence of red green and blue exposures through a rotating filter cum shutter“. Source: Coote, Jack H. (1993): The Illustrated History of Colour Photography. Surbiton, Surrey: Fountain Press.
- „In 1899 Lee and Turner obtained a patent for a three colour process of cinematography requiring a single lens camera […] making a recurring sequence of red green and blue exposures through a rotating filter cum shutter“. Source: Coote, Jack H. (1993): The Illustrated History of Colour Photography. Surbiton, Surrey: Fountain Press.
- „Their projector […] used three lenses and a special filter wheel which enabled every frame of the film to be projected three times in succession through the appropriate filter as it passed through the triple frame projector aperture. Although it eventually led to the Kinemacolor two colour process, the Lee and Turner patent was not successful“. Source: Coote, Jack H. (1993): The Illustrated History of Colour Photography. Surbiton, Surrey: Fountain Press.
- National Media Museum, UK. Lee and Turner Colour Projector, 1902.
- Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
- Illustration of the process from National Media Museum's short documentary.
- 38 mm positive of the Lee Turner film showing the three b/w images for the three color records. Credit: Brian Pritchard.
16 Images in 1 Gallery
Photographs of unidentified color film technologies. Several different principles and times. Feel free to contact us if you can help identifying them!
-
![]() Unidentified Processes from the Kodak Film Samples Collection and the Cinematography Collection.
Credit: National Science and Media Museum Bradford.
Photographs by Barbara Flueckiger in collaboration with Noemi Daugaard, SNSF Film Colors.
Unidentified Processes from the Kodak Film Samples Collection and the Cinematography Collection.
Credit: National Science and Media Museum Bradford.
Photographs by Barbara Flueckiger in collaboration with Noemi Daugaard, SNSF Film Colors.
- Unidentified Processes from the Kodak Film Samples Collection and the Cinematography Collection. Credit: National Science and Media Museum Bradford. Photographs by Barbara Flueckiger in collaboration with Noemi Daugaard, SNSF Film Colors.
- Unidentified Processes from the Kodak Film Samples Collection and the Cinematography Collection. Credit: National Science and Media Museum Bradford. Photographs by Barbara Flueckiger in collaboration with Noemi Daugaard, SNSF Film Colors.
298 Images in 5 Galleries
-
![]() Source: Coe, Brian (1978): Colour Photography. The First Hundred Years 1840-1940. London: Ash & Grant, p. 54.
Source: Coe, Brian (1978): Colour Photography. The First Hundred Years 1840-1940. London: Ash & Grant, p. 54.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 34.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 35.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 35.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 36.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 74.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 74.
7 Images
-
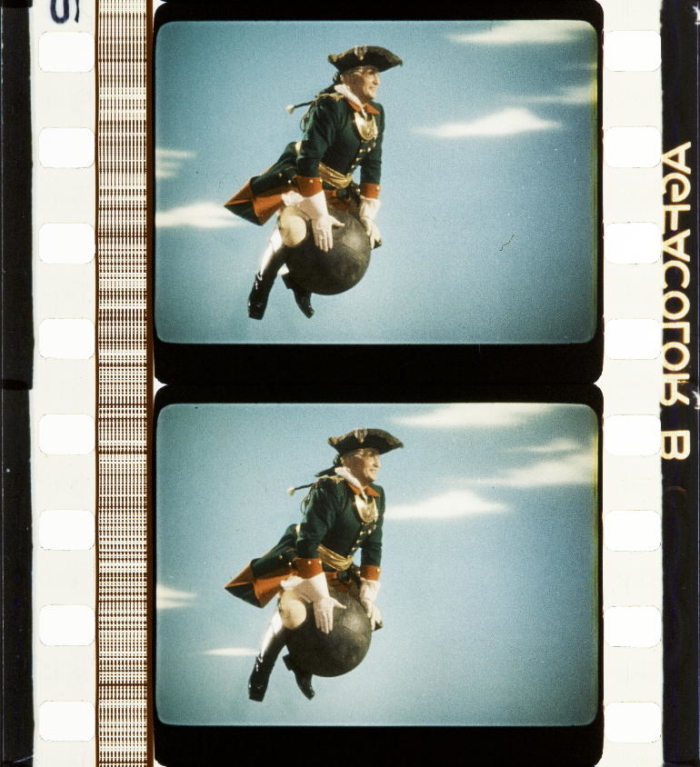
![]() Casanova (FRA 1927, Alexandre Volkoff). Credit: Cinémathèque française. Photographs of the stencil colored safety print by Barbara Flueckiger.
Casanova (FRA 1927, Alexandre Volkoff). Credit: Cinémathèque française. Photographs of the stencil colored safety print by Barbara Flueckiger.
-
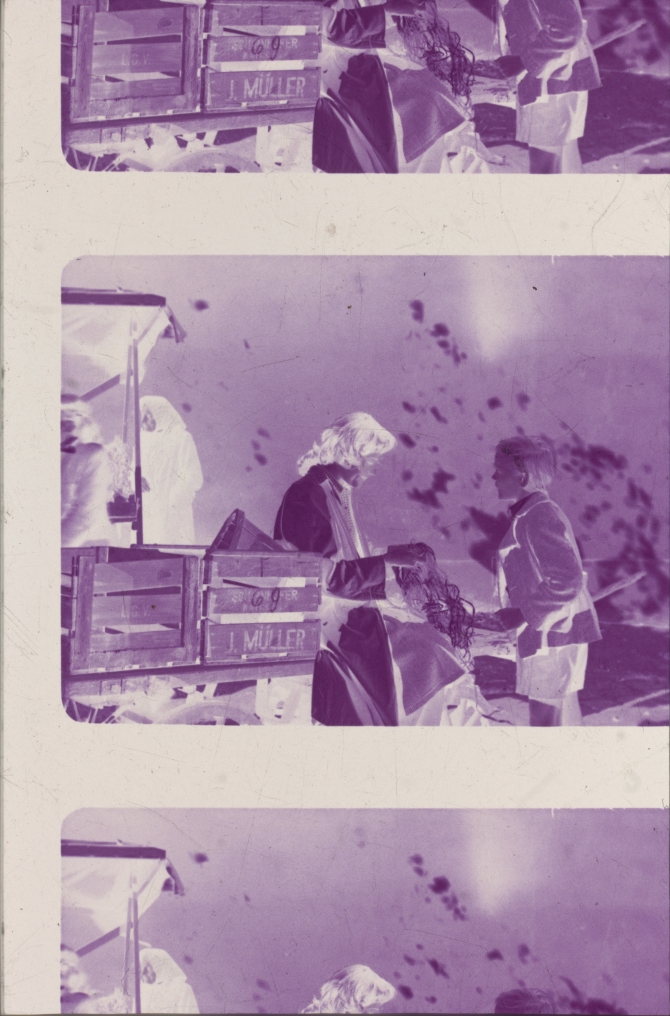
Print no. 1 of Amour d'esclave (FRA 1907, Albert Capellani). Credit: Library of Congress. Photograph of the nitrate film print by Barbara Flueckiger.
Edge mark: Pathé (April 1907-1909), on one edge, PATHÉ FRÈRES and on the other, 14 RUE FAVART PARIS (partially visible). Cf. Ill.PM.4: Brown, Harold (1990): Physical Characteristics of Early Films as Aids to Identification. Brussels: FIAF, on p. 9.
- Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
- Source: Coe, Brian (1981): The History of Movie Photography. Westfield, N.J.: Eastview Editions.
-
Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: Amour d'esclave (France 1907).
Edge mark: PATHÉ FRÈRES PARIS (without gap, 1906-1907, partially visible). Cf.: Ill.PM.33: Brown, Harold (1990): Physical Characteristics of Early Films as Aids to Identification. Brussels: FIAF, on p. 9.
View Quote on Page: Edge Codes and Identification
Trade mark in scene: Pathé cockerel (until 1909). Cf.: Ill.TM.5: Brown 1990: on p. 30.
- Tinting in combination with stencil coloring. Credit: Turconi Collection by courtesy of George Eastman House Motion Picture Department Collection. Film: L'Exode (FRA 1910, Louis Feuillade)
- Credit: Turconi Collection by courtesy of George Eastman House Motion Picture Department Collection. Film: L'Exode (FRA 1910, Louis Feuillade)
-
Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: Le Pied de Mouton (ca. 1910).
Edge mark: Pathé (1909 onward), on one edge, PATHÉ FRÈRES 14 RUE FAVART PARIS and on the other, EXHIBITION INTERDITE EN FRANCE EN SUISSE ET EN BELGIQUE (partially visible). Cf.: Ill.PM.5: Brown, Harold (1990): Physical Characteristics of Early Films as Aids to Identification. Brussels: FIAF, on p. 9.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Golden Beetle (1907).
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: Unknown film (ca. 1919).
- Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
- Credit: Cineteca di Bologna.
- Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. In: Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Credit: Turconi Collection by courtesy of George Eastman Museum, Motion Picture Department Collection. Film: Kinder-Karno in Nizza.
- Toplight and backlight, Swiss collector's copy. Source: Didiée, L. (1926): Le Film vierge Pathé. Manuel de développement et de tirage. Paris: Pathé.
- Backlight, Swiss collector's copy. Source: Didiée, L. (1926): Le Film vierge Pathé. Manuel de développement et de tirage. Paris: Pathé.
- Toplight and backlight, Swiss collector's copy. Source: Didiée, L. (1926): Le Film vierge Pathé. Manuel de développement et de tirage. Paris: Pathé.
- Toplight and backlight, Swiss collector's copy. Source: Didiée, L. (1926): Le Film vierge Pathé. Manuel de développement et de tirage. Paris: Pathé.
- Pathéorama. Toplight and backlight, Swiss collector's copy. Source: Didiée, L. (1926): Le Film vierge Pathé. Manuel de développement et de tirage. Paris: Pathé.
- Pathéorama. Backlight, Swiss collector's copy. Source: Didiée, L. (1926): Le Film vierge Pathé. Manuel de développement et de tirage. Paris: Pathé.
- Pathéorama. Credit: Clayton Scoble and Stephen Jennings, Harvard University, Fine Arts Library. Backlight. Source: Didiée, L. (1926): Le Film vierge Pathé. Manuel de développement et de tirage. Paris: Pathé.
- Credit: Clayton Scoble and Stephen Jennings, Harvard University, Fine Arts Library. Backlight. Source: Didiée, L. (1926): Le Film vierge Pathé. Manuel de développement et de tirage. Paris: Pathé.
2193 Images in 73 Galleries
-
![]() Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
- Source: Wall, E.J. (1925): The History of Three-color Photography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
2 Images
-
![]() Cyan and magenta combined, third layer, yellow missing. Source: Meister Lucius & Brüning (1905): Pinatypie. Positiv-Verfahren für die Dreifarbenphotographie. Höchst am Main.
Cyan and magenta combined, third layer, yellow missing. Source: Meister Lucius & Brüning (1905): Pinatypie. Positiv-Verfahren für die Dreifarbenphotographie. Höchst am Main.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 235.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 235.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 132.
4 Images
-
![]() Source: Wall, E.J. (1925): The History of Three-color Photography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
Source: Wall, E.J. (1925): The History of Three-color Photography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
1 Image
-
![]() Photomicrograph (50x) of an Autochrome mosaic screen. Credit: Courtesy of George Eastman House, International Museum of Photography and Film.
Photomicrograph (50x) of an Autochrome mosaic screen. Credit: Courtesy of George Eastman House, International Museum of Photography and Film.
- Source: Lavédrine, Bertrand (2009): Photographs of the Past. Process and Preservation. Los Angeles: Getty Publications.
- Source: Coote, Jack H. (1993): The Illustrated History of Colour Photography. Surbiton, Surrey: Fountain Press.
- Source: Coote, Jack H. (1993): The Illustrated History of Colour Photography. Surbiton, Surrey: Fountain Press.
- Source: Holme, Charles (1908): Colour Photography, and Other Recent Developments of the Art of the Camera. London, Paris, New York.: Offices of The Studio.
- Source: Holme, Charles (1908): Colour Photography, and Other Recent Developments of the Art of the Camera. London, Paris, New York.: Offices of The Studio.
- Credit: Klosterarchiv Einsiedeln. http://www.klosterarchiv.ch/earchiv_liste.php?Objektyp_physisch=Glasautochrom&start=1
- Credit: Klosterarchiv Einsiedeln. http://www.klosterarchiv.ch/earchiv_liste.php?Objektyp_physisch=Glasautochrom&start=1
- Credit: Klosterarchiv Einsiedeln. http://www.klosterarchiv.ch/earchiv_liste.php?Objektyp_physisch=Glasautochrom&start=1
- Credit: Klosterarchiv Einsiedeln. http://www.klosterarchiv.ch/earchiv_liste.php?Objektyp_physisch=Glasautochrom&start=1
- Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 70.
- Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 26.
- Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 65.
- Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 27.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 235.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 64.
16 Images
-
![]() Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 161.
Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 161.
1 Image
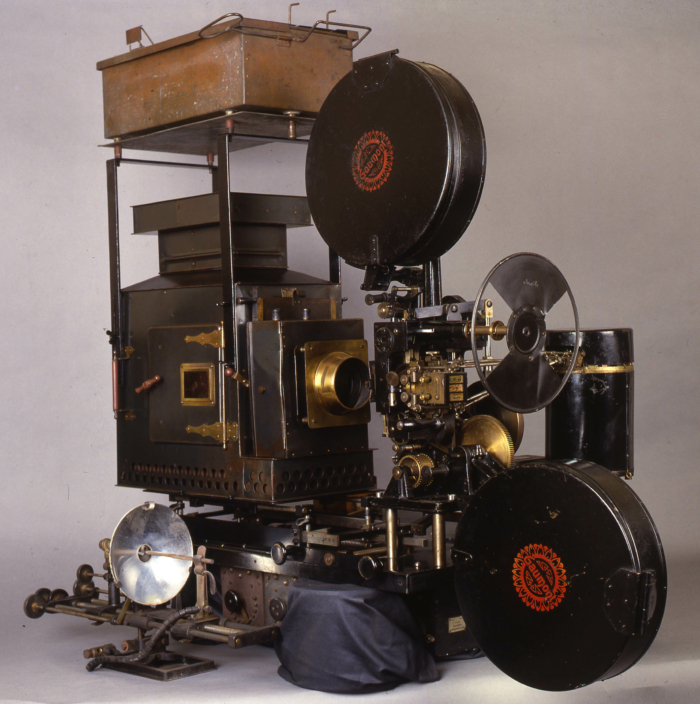
Kinemacolor was an additive process operated with alternating red and green filters that were applied to the shutter in front of the camera and in front of the projector. With at least 32 fps the frame rate was double the minimal frame rate of 16 fps. Time parallax with small differences between the red and green record resulted in color fringes that became visible when objects or scenes were moving.
-
![]() Kinemacolor projector used for David Cleveland's and Brian Pritchard's reconstruction. Credit: Brian Pritchard.
Kinemacolor projector used for David Cleveland's and Brian Pritchard's reconstruction. Credit: Brian Pritchard.
13 Images in 3 Galleries
-
![]() Coote, Jack H. (1993): The Illustrated History of Colour Photography. Surbiton, Surrey: Fountain Press,
Coote, Jack H. (1993): The Illustrated History of Colour Photography. Surbiton, Surrey: Fountain Press,
- Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
- Source: Ede, François (1994): Jour de fête ou la couleur retrouvée. Cahiers du Cinéma: Paris.
- Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 71.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 73.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 31.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 32.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 33.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 48.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 69.
10 Images
-
![]() Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
- Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Ede, François (1994): Jour de fête ou la couleur retrouvée. Cahiers du Cinéma: Paris.
- Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
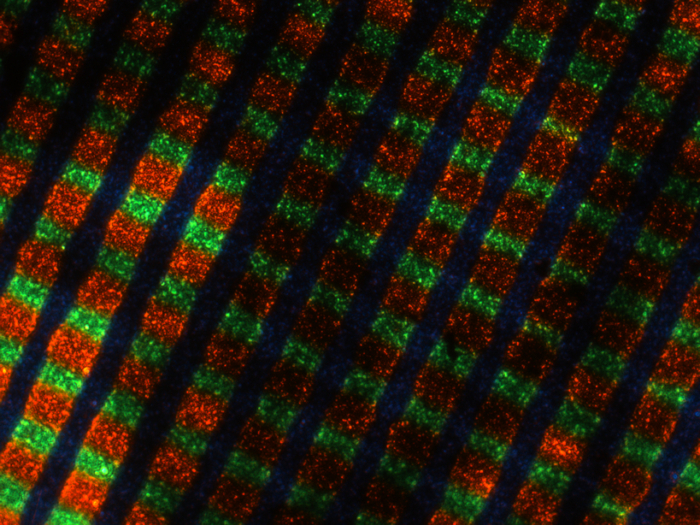
- Source: Heymer, Gerd (1933): Auflösungsvermögen und Farbwiedergabe in der Farbrasterphotographie. In: Veröffentlichungen des wissenschaftlichen Zentral-Laboratoriums der photographischen Abteilung Agfa, 3, 1933, pp. 188-207.
4 Images
-
![]() Virages sur mordançage, Bleu (blue mordant toning), backlight, Swiss collectors'copy. Source: Didiée, L. (1926): Le Film vierge Pathé. Manuel de développement et de tirage. Paris: Pathé. [quote id='7']
Virages sur mordançage, Bleu (blue mordant toning), backlight, Swiss collectors'copy. Source: Didiée, L. (1926): Le Film vierge Pathé. Manuel de développement et de tirage. Paris: Pathé. [quote id='7']
- Photomicrograph, 25x. Credit: Norbert Wey, Institute of Pathology, University of Zurich.
- Photomicrograph, 50x. Credit: Norbert Wey, Institute of Pathology, University of Zurich.
- Photomicrograph, 100x. Credit: Norbert Wey, Institute of Pathology, University of Zurich.
- Photomicrograph, 100x. Credit: Norbert Wey, Institute of Pathology, University of Zurich.
171 Images in 7 Galleries
-
![]() Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
3 Images in 1 Gallery
-
![]() Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
- Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
2 Images
-
![]() Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press, p. 67.
Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press, p. 67.
1 Image
-
![]() Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
- Source: Ede, François (1994): Jour de fête ou la couleur retrouvée. Cahiers du Cinéma: Paris.
- Credit: Paolo Cherchi Usai. Source: Cherchi Usai, Paolo (2000): Silent Cinema. London: BFI.
- Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Ede, François (1994): Jour de fête ou la couleur retrouvée. Cahiers du Cinéma: Paris.
- Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
- Source: Gaumont, Léon (1959): Gaumont Chronochrome Process Described by the Inventor. In: Raymond Fielding (ed.): A Technological History of Motion Pictures and Television. An Anthology from the Pages of The Journal of the Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers. Berkeley; Los Angeles: University of California Press, 1967, pp. 65-67.
- Source: Gaumont, Léon (1959): Gaumont Chronochrome Process Described by the Inventor. In: Raymond Fielding (ed.): A Technological History of Motion Pictures and Television. An Anthology from the Pages of The Journal of the Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers. Berkeley; Los Angeles: University of California Press, 1967, pp. 65-67.
12 Images in 2 Galleries
-
![]() Credit: Courtesy of BFI National Archive. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger. Film: Cinechrome Colour Test with Soap Boxes and Packets (1920)
Credit: Courtesy of BFI National Archive. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger. Film: Cinechrome Colour Test with Soap Boxes and Packets (1920)
- Credit: Courtesy of BFI National Archive. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger. Film: Cinechrome Colour Test with Soap Boxes and Packets (1920)
- Credit: Courtesy of BFI National Archive. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger. Film: Cinechrome Colour Test with Soap Boxes and Packets (1920)
3 Images
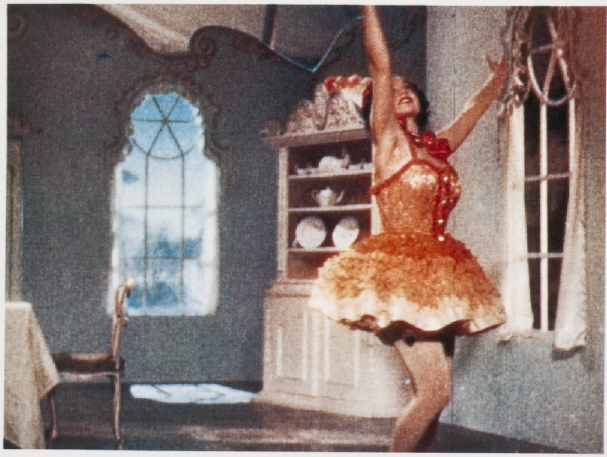
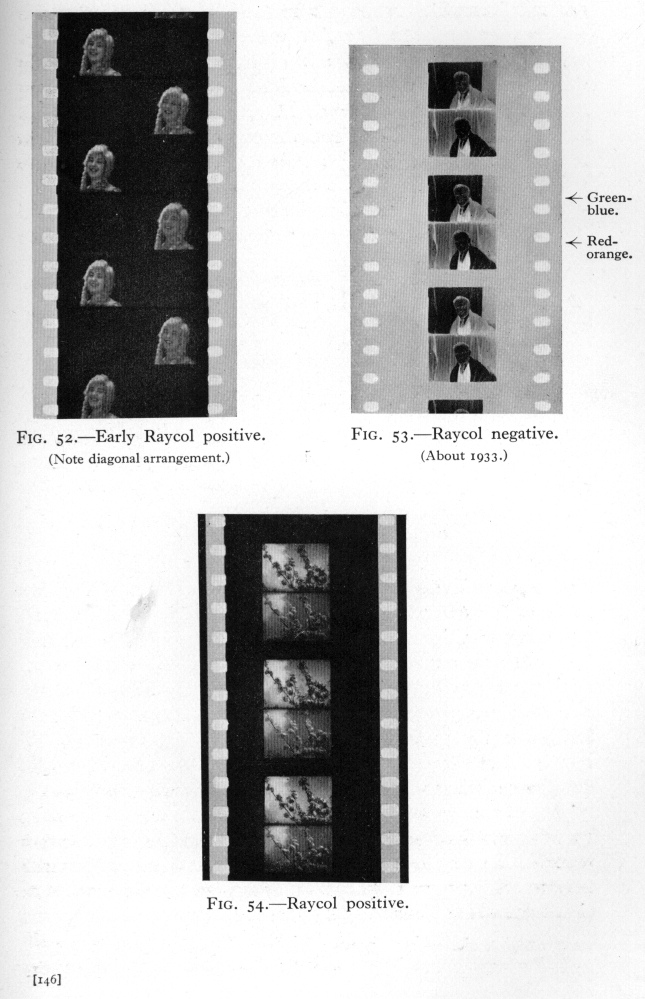
The Kodachrome process was invented in 1913 by John G. Capstaff for still photography and subsequently adapted to motion pictures. For the process two frames were advanced simultaneously, one located above the other. The light passed either through two lenses or through a beam-splitter, fitted with red and green filters. The release print was exposed through a beam-splitter whereby the alternate frames were projected onto either side of double-coated stock. After development by a usual b/w process, the film was tanned to harden the exposed areas. The soft areas were dyed red-orange and blue-green respectively.
-
![]() Two-Color Kodachrome Print (USA ca. 1925 to 1927, Anonymous). Credit: George Eastman Museum. Photographs of the Kodachrome two-color double coated stock from 1925 and 1927 by Olivia Kristina Stutz, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors.
Two-Color Kodachrome Print (USA ca. 1925 to 1927, Anonymous). Credit: George Eastman Museum. Photographs of the Kodachrome two-color double coated stock from 1925 and 1927 by Olivia Kristina Stutz, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors.
- Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. In:Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Magnification 5x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Magnification 10x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Magnification 20x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Kodachrome Two-color test from 1922, YouTube channel of the George Eastman House.
350 Images in 12 Galleries
-
![]() Black-and-white with Handschiegl in Lights of Old Broadway (USA 1925, Monta Bell). Credit: Library of Congress. Photograph of the nitrate print by Barbara Flueckiger.
Black-and-white with Handschiegl in Lights of Old Broadway (USA 1925, Monta Bell). Credit: Library of Congress. Photograph of the nitrate print by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: Trail of '98 (USA 1929, Clarence Brown).
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: Trail of '98 (USA 1929, Clarence Brown).
- Credit: Paolo Cherchi Usai. Source: Cherchi Usai, Paolo (2000): Silent Cinema. London: BFI. Film: Greed (USA 1925, Erich von Stroheim).
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: Forbidden Fruit (USA 1921, Cecil B. DeMille).
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: Forbidden Fruit (USA 1921, Cecil B. DeMille).
- Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press, p. 24.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: Trail of '98 (USA 1929, Clarence Brown).
141 Images in 8 Galleries
-
![]() Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press. Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press. Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
- Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
- Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press. Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
3 Images
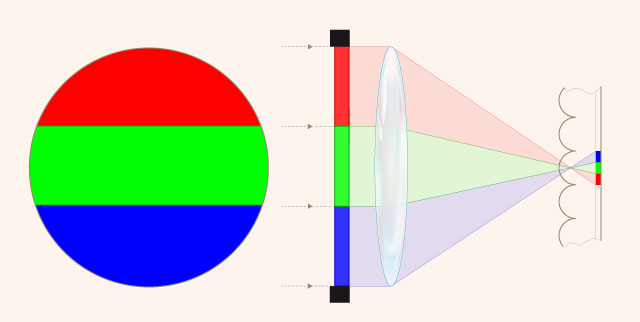
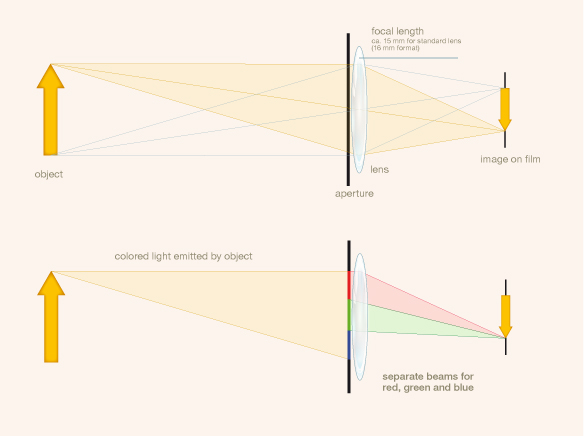
During the capturing of the film a beam-splitter in combination with filters in the camera divided the incoming light into a red and a green separation negative on black-and-white stock. When projected in the cinema the two images were combined simultaneously by additive mixture through corresponding red and green filters into one picture consisting of red and green colored light. The reduction of the whole color range to two colors (and their additive combinations) was necessary because of the complex optical arrangement.
-
![]() The beam-splitter prism. Source: Coote, Jack H. (1993): The Illustrated History of Colour Photography. Surbiton, Surrey: Fountain Press.
The beam-splitter prism. Source: Coote, Jack H. (1993): The Illustrated History of Colour Photography. Surbiton, Surrey: Fountain Press.
6 Images in 1 Gallery
-
![]() Magnification. Source: Coe, Brian (1978): Colour Photography. The First Hundred Years 1840-1940. London: Ash & Grant.
Magnification. Source: Coe, Brian (1978): Colour Photography. The First Hundred Years 1840-1940. London: Ash & Grant.
- Source: Coote, Jack H. (1993): The Illustrated History of Colour Photography. Surbiton, Surrey: Fountain Press.
- Source: Heymer, Gerd (1943): Die neuere Entwicklung der Farbphotographie. In: Ergänzungswerk zum Handbuch der wissenschaftlichen und angewandten Photographie. Wien: Julius Springer 1943, pp. 337-463.
- Source: Finger, Ehrhard (1998): Die Pioniere des Wolfener Farbfilms. In: Industrie- und Filmmuseum Wolfen e. V. (ed.), Die Filmfabrik Wolfen. Aus der Geschichte, Heft 2, pp. 16-36. (in German) [quote id='4']
- Source: Finger, Ehrhard (1998): Die Pioniere des Wolfener Farbfilms. In: Industrie- und Filmmuseum Wolfen e. V. (ed.), Die Filmfabrik Wolfen. Aus der Geschichte, Heft 2, pp. 16-36. (in German) [quote id='4']
- Source: Finger, Ehrhard (1998): Die Pioniere des Wolfener Farbfilms. In: Industrie- und Filmmuseum Wolfen e. V. (ed.), Die Filmfabrik Wolfen. Aus der Geschichte, Heft 2, pp. 16-36. (in German) [quote id='4']
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 73.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 73.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 72.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 72.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 42.
11 Images
-
![]() Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
- Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
2 Images
-
![]() Knowing Men (GB 1930, Elinor Glyn), negative. Credit: Courtesy of BFI National Archive. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
Knowing Men (GB 1930, Elinor Glyn), negative. Credit: Courtesy of BFI National Archive. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
3 Images in 1 Gallery
-
![]() Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
1 Image
-
![]() Polychromide samples from the Kodak Film Samples Collection at the National Science and Media Museum in Bradford.
Credit: National Science and Media Museum Bradford.
Photographs by Barbara Flueckiger in collaboration with Noemi Daugaard.
Polychromide samples from the Kodak Film Samples Collection at the National Science and Media Museum in Bradford.
Credit: National Science and Media Museum Bradford.
Photographs by Barbara Flueckiger in collaboration with Noemi Daugaard.
- Credit: Brian Pritchard
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 279.
66 Images in 2 Galleries
-
![]() The two colors visible at a splice. Credit: EYE Film Institute Amsterdam. Film: [Kleurenpracht].
The two colors visible at a splice. Credit: EYE Film Institute Amsterdam. Film: [Kleurenpracht].
- Credit: George Eastman House. Preserved by Carole Fodor, Haghefilm Digitaal fellow and graduate of The L. Jeffrey Selznick School of Film Preservation. Film: A Day with John Burroughs (Prizma, 1919).
- Credit: George Eastman House. Preserved by Carole Fodor, Haghefilm Digitaal fellow and graduate of The L. Jeffrey Selznick School of Film Preservation. Film: A Day with John Burroughs (Prizma, 1919).
- Credit: George Eastman House Motion Picture Department Collection. Film: The Land of the Great Spirit (1919).
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Orange.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Orange.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Orange.
399 Images in 14 Galleries
-
![]() Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
- Source: Coe, Brian (1981): The History of Movie Photography. Westfield, N.J.: Eastview Editions.
- Credit: Collection Gert Koshofer, Bergisch Gladbach (Germany).
16 Images in 1 Gallery
The first subtractive 2 color process introduced by Technicolor captured the incoming light through a beam splitter with red and green filters also. However, in contrast to the first Technicolor process, the two b/w images were recorded on one negative strip. This was achieved by the pull-down of two frames simultaneously, a process that required the double speed in the camera. These two frames were arranged in pairs, whereby the green record was inverted up-side down (see image).
-
![]() The Phantom of the Opera (USA 1925, Rupert Julian). Credit: UCLA Film & Television Archive. Photographs of the nitrate print by Barbara Flueckiger.
The Phantom of the Opera (USA 1925, Rupert Julian). Credit: UCLA Film & Television Archive. Photographs of the nitrate print by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Credit: Images courtesy of the Margaret Herrick Library. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Source: Coe, Brian (1981): The History of Movie Photography. Westfield, N.J.: Eastview Editions.
- Apparently test pieces, these clippings may well be the oldest surviving samples of the process in existence. Ruedel (2009: 55). Credit: George Eastman House Motion Picture Department Collection. Source: Ruedel, Ulrich (2009): The Technicolor Notebooks at the George Eastman House. In: Film History, Volume 21, Number 1, 2009, pp. 47-60.
- Apparently test pieces, these clippings may well be the oldest surviving samples of the process in existence. Ruedel (2009: 55); color reconstruction of the images shown above. Credit: George Eastman House Motion Picture Department Collection. Source: Ruedel, Ulrich (2009): The Technicolor Notebooks at the George Eastman House. In: Film History, Volume 21, Number 1, 2009, pp. 47-60.
- Apparently test pieces, these clippings may well be the oldest surviving samples of the process in existence. Ruedel (2009: 55). Credit: George Eastman House Motion Picture Department Collection. Source: Ruedel, Ulrich (2009): The Technicolor Notebooks at the George Eastman House. In: Film History, Volume 21, Number 1, 2009, pp. 47-60.
- Arrangement of the two records on the camera negative. Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress.
- Film: Stage Struck (USA 1925, Allan Dwan). Credit: Nitrate Frame Collection. George Eastman House Moving Image Collection. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Film: Irene (USA 1926, Alfred E. Green). Credit: Nitrate Frame Collection. George Eastman House Moving Image Collection. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Film: Irene (USA 1926, Alfred E. Green). Credit: Library of Congress. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Film: Irene (USA 1926, Alfred E. Green). Credit: Library of Congress. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Film: Irene (USA 1926, Alfred E. Green). Credit: Library of Congress. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Film: Irene (USA 1926, Alfred E. Green). Credit: Library of Congress. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Film: Irene (USA 1926, Alfred E. Green). Credit: Library of Congress. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
133 Images in 8 Galleries
-
![]() Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 103.
Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 103.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 277.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 138.
3 Images
-
![]() Russian Ideas in Clothes! (USA 1922). Credit: UCLA Film & Television Archive. Photographs of the nitrate print by Barbara Flueckiger.
Russian Ideas in Clothes! (USA 1922). Credit: UCLA Film & Television Archive. Photographs of the nitrate print by Barbara Flueckiger.
21 Images in 1 Gallery
-
![]() Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
- Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
- Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
- Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Ede, François (1994): Jour de fête ou la couleur retrouvée. Cahiers du Cinéma: Paris.
- Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
- Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
- Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
- Microscopic image of a piece of Keller-Dorian lenticular film embedded in epoxide resin. The 3-dimensional structure of the lenticules is visible as well as the thin emulsion layer on the other side of the acetate base. Credit: Sample preparation and imaging by the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.
- Lenticular surface of the acetate plastic base of Keller-Dorian lenticular film. On the back plane of the acetate layer and therefore out of focus in this image, structures defined by the silver image in the emulsion layer can be perceived. Credit: David Pfluger, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors. Imaging was performed with support of the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.
- Hexagonal structure of the lenticules of Keller-Dorian lenticular film. Credit: David Pfluger, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors. Imaging was performed with support of the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.
- Microscopic images of the Keller-Dorian lenticular structure with the focus set at different points. The images have been chained to show a travelling through the 3-dimensional structure of the bee-hive shaped lenticules. Credit: David Pfluger, conversion to video by Martin Weiss, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors. Imaging was performed with support of the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.
14 Images in 2 Galleries
-
![]() Credit: George Eastman House Motion Picture Department Collection. Film: The Old Family Toothbrush (USA 1925).
Credit: George Eastman House Motion Picture Department Collection. Film: The Old Family Toothbrush (USA 1925).
1 Image
-
![]() Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 73.
Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 73.
1 Image
-
![]() Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
- Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
2 Images
-
![]() Magnification 20x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
Magnification 20x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Magnification 10x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Magnification 5x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. In: Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Source: Coe, Brian (1981): The History of Movie Photography. Westfield, N.J.: Eastview Editions.
- Magnification of an image area. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
78 Images in 2 Galleries
-
![]() Credit: Gert Koshofer Collection. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
Credit: Gert Koshofer Collection. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
- Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
5 Images in 1 Gallery
The third Technicolor process used the same camera as process no. II to combine a pair of frames of the red and green record respectively on the b/w negative (see image). In contrast to the former process, however, the two images were printed on one side of the positive by the dye transfer or imbibition process.
-
![]() King of Jazz (USA 1930, John Murray Anderson). Credit: Library of Congress. Photographs of the Technicolor No. III dye-tranfer nitrate print from 1930 and 1931 by Olivia Kristina Stutz, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors.
King of Jazz (USA 1930, John Murray Anderson). Credit: Library of Congress. Photographs of the Technicolor No. III dye-tranfer nitrate print from 1930 and 1931 by Olivia Kristina Stutz, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors.
- Credit: Images courtesy of the Margaret Herrick Library. Film: Corrine Griffith in The Garden of Eden. Photograph: Barbara Flueckiger.
- Credit: George Eastman House Motion Picture Department Collection. Film: Buffalo Bill’s Last Fight (USA 1927, John W. Noble).
- Technicolor ad in Photoplay, 1930. Source: Photoplay, 1930, see Media History Digital Library
- Technicolor ad in Photoplay, 1930. Source: Photoplay, 1930, see Media History Digital Library
- Photomicrograph, 10x. Credit: Silvana Konermann.
- Photomicrograph, 20x. Credit: Silvana Konermann.
- Doctor X (USA 1932, Michael Curtiz). Credit: UCLA Film & Television Archive. Photographs of the Technicolor No. III dye-tranfer nitrate print by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Doctor X (USA 1932, Michael Curtiz). Credit: UCLA Film & Television Archive. Photographs of the Technicolor No. III dye-tranfer nitrate print by Barbara Flueckiger.
1298 Images in 38 Galleries
-
![]() Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress.
Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress.
2 Images
-
![]() Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 74.
Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 74.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 44.
2 Images
-
![]() Kodacolor lenticular filter for the projector. Lichtspiel / Kinemathek Bern.
Kodacolor lenticular filter for the projector. Lichtspiel / Kinemathek Bern.
- Credit: Rudolf Gschwind, Imaging and Media Lab, University of Basel.
- Magnification of an area. Credit: Rudolf Gschwind, Imaging and Media Lab, University of Basel.
- Color reconstruction test. Credit: Rudolf Gschwind, Imaging and Media Lab, University of Basel.
- Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
- Microscopic linear lens structure of Kodacolor lenticular film. Credit: David Pfluger, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors. Imaging was performed with support of the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.
- Acetate plastic base of Kodacolor lenticular film embedded in epoxide resin. The emulsion layer usually placed on the opposite side of the acetate base has been removed beforehand and is therefore not visible. Credit: David Pfluger, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors. Imaging was performed with support of the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.Credit: David Pfluger, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors. Imaging was performed with support of the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.
- Focal travelling through the 3-dimensional structure of Kodacolor lenticular film. In the beginning the linear lenticular structure is visible and towards the end the emulsion layer comes into focus and the granular structure defined by the density of the silver is visible. In this shot the lenticules were showing towards the light source and the emulsion towards the camera. This enables an undistorted recording of the emulsion layer. Credit: David Pfluger, editing by Martin Weiss, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors. Imaging was performed with support of the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.
- Focal travelling through the 3-dimensional structure of Kodacolor lenticular film. In the beginning the linear lenticular structure is visible and towards the end the emulsion layer comes into focus. In this shot the lenticules were allocated towards the lens of the microscope and the light source at the side of the emulsion similar to the configuration in projection. As a consequence the graininess of the emulsion is not visible as with the film flipped to the other side. The structure is optically distorted perpendicular to the linear structure of the lenticules. Credit: David Pfluger, editing by Martin Weiss, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors. Imaging was performed with support of the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.
24 Images in 1 Gallery
-
![]() Iridescence on Multicolor print, reflection properties. Credit: Library of Congress. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger
Iridescence on Multicolor print, reflection properties. Credit: Library of Congress. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger
- Magnification 20x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Magnification 10x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Magnification 5x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: Fox Movietone Follies of 1929.
- Source: Coe, Brian (1981): The History of Movie Photography. Westfield, N.J.: Eastview Editions.
- Source: Cornwell-Clyne, Adrian (1951): Colour Cinematography. London: Chapman & Hall.
- Source: Cornwell-Clyne, Adrian (1951): Colour Cinematography. London: Chapman & Hall.
- Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Cornwell-Clyne, Adrian (1951): Colour Cinematography. London: Chapman & Hall.
- Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Magnification of an area. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Reflection properties. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
72 Images in 6 Galleries
-
![]() Credit: Paolo Cherchi Usai. Source: Cherchi Usai, Paolo (2000): Silent Cinema. London: BFI.
Credit: Paolo Cherchi Usai. Source: Cherchi Usai, Paolo (2000): Silent Cinema. London: BFI.
- Source: The International Photographer, July 1929
- Source: The International Photographer, July 1929
- Source: The International Photographer, July 1929
- Source: The International Photographer, July 1929
79 Images in 3 Galleries
-
![]() Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Cinécolor, mosaic screen, ca. 1929. Credit: Gert Koshofer Collection. Sample No. 68. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
- Magnification of an image area. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
27 Images in 2 Galleries
-
![]() Credit: Technicolor Collection. George Eastman House Moving Image Department. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
Credit: Technicolor Collection. George Eastman House Moving Image Department. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Credit: Technicolor Collection. George Eastman House Moving Image Department. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Credit: Technicolor Collection. George Eastman House Moving Image Department. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
3 Images
-
![]() Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
13 Images in 1 Gallery
-
![]() Magnification, 20x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
Magnification, 20x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Magnification, 10x. Credit: Photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Magnification, 5x. Credit: Photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. In: Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Magnification of an image area. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Reflection on the Sirius film, front. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Reflection on the Sirius film, back. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
142 Images in 4 Galleries
-
![]() Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
11 Images in 1 Gallery
-
![]() Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 70.
Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 70.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 70.
- Photomicrograph (20x) of a Finlay screen. Credit: Courtesy of George Eastman House, International Museum of Photography and Film.
- Finlay box. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 39.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 39.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 40.
9 Images in 1 Gallery
-
![]() Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
42 Images
-
![]() Strange Birds (US 1930, Mack Sennett). Credit: Library of Congress. Photograph of the nitrate print: Barbara Flueckiger
Strange Birds (US 1930, Mack Sennett). Credit: Library of Congress. Photograph of the nitrate print: Barbara Flueckiger
- Magnification. Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: Strange Birds (1930)
18 Images in 1 Gallery
-
![]() Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
1 Image
-
![]() Dyes of Brewster color. Credit: Brian Pritchard.
Dyes of Brewster color. Credit: Brian Pritchard.
- Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
52 Images in 1 Gallery
-
![]() Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
- Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
- Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
3 Images
-
![]() Rotating filters permitting to adjust tonality and intensity of the colors. Source: Pierotti, Federico (2016): Un'archeologia del colore nel cinema italiano. Dal Technicolor ad Antonioni. Pisa: Edizioni ETS, p. 62
Rotating filters permitting to adjust tonality and intensity of the colors. Source: Pierotti, Federico (2016): Un'archeologia del colore nel cinema italiano. Dal Technicolor ad Antonioni. Pisa: Edizioni ETS, p. 62
1 Image
-
![]() Magnification of an image area. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
Magnification of an image area. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Color chart. Credit: Guido Seeber Nachlass, Deutsche Kinemathek, Berlin. Source: Goergen, Jeanpaul (2010): Rotorange und blaugrün. Das Zweifarbenverfahren Ufacolor 1931-1940. In: Filmblatt, no. 43, pp. 77-92.
- Credit: Guido Seeber Nachlass, Deutsche Kinemathek, Berlin. Source: Goergen, Jeanpaul (2010): Rotorange und blaugrün. Das Zweifarbenverfahren Ufacolor 1931-1940. In: Filmblatt, no. 43, pp. 77-92.
- Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Credit: Bundesarchiv-Filmarchiv, photo: Marian Stefanowski. Source: Goergen, Jeanpaul (2010): Rotorange und blaugrün. Das Zweifarbenverfahren Ufacolor 1931-1940. In: Filmblatt, no. 43, pp. 77-92. Film: Bunte Tierwelt. Studien in Hagebecks Tierpark in Stellingen (1931).
- Credit: Bundesarchiv-Filmarchiv, photo: Marian Stefanowski. Source: Goergen, Jeanpaul (2010): Rotorange und blaugrün. Das Zweifarbenverfahren Ufacolor 1931-1940. In: Filmblatt, no. 43, pp. 77-92. Film: Karneval (1936).
- Credit: Bundesarchiv-Filmarchiv, photo: Jeanpaul Goergen. Source: Goergen, Jeanpaul (2010): Rotorange und blaugrün. Das Zweifarbenverfahren Ufacolor 1931-1940. In: Filmblatt, no. 43, pp. 77-92. Film: Bunte Fischwelt (1936).
- Credit: Bundesarchiv-Filmarchiv, photo: Marian Stefanowski. Source: Goergen, Jeanpaul (2010): Rotorange und blaugrün. Das Zweifarbenverfahren Ufacolor 1931-1940. In: Filmblatt, no. 43, pp. 77-92. Film: Karneval (1936).
- Credit: Deutsches Filminstitut DIF (Vicas Nachlass), photo: Jeanpaul Goergen. Source: Goergen, Jeanpaul (2010): Rotorange und blaugrün. Das Zweifarbenverfahren Ufacolor 1931-1940. In: Filmblatt, no. 43, pp. 77-92. Film: Potsdam (1934).
- Credit: Bundesarchiv-Filmarchiv, photo: Marian Stefanowski. Source: Goergen, Jeanpaul (2010): Rotorange und blaugrün. Das Zweifarbenverfahren Ufacolor 1931-1940. In: Filmblatt, no. 43, pp. 77-92. Film: Farben machen froh (1938).
- Magnification 5x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Magnification 10x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Magnification 20x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. In:Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Magnification of an image area. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. In:Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Reflection on Ufacolor film. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. In:Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- An opened splice of an Ufacolor positive shows the two colors used in the process. Credit: David Pfluger. Source: David Pfluger’s collection.
136 Images in 7 Galleries
-
![]() Source: Cornwell-Clyne, Adrian (1951): Colour Cinematography. London: Chapman & Hall.
Source: Cornwell-Clyne, Adrian (1951): Colour Cinematography. London: Chapman & Hall.
- Source: Cornwell-Clyne, Adrian (1951): Colour Cinematography. London: Chapman & Hall.
2 Images
-
![]() Mysore Yesterday and Tomorrow Credit: Image courtesy of the 20th Century Fox Collection at the Academy Film Archive. Photograph: Barbara Flueckiger.
Mysore Yesterday and Tomorrow Credit: Image courtesy of the 20th Century Fox Collection at the Academy Film Archive. Photograph: Barbara Flueckiger.
23 Images in 2 Galleries
-
![]() Rota Farbenfilm Samples (Kodak Film Samples Collection). Credit: National Science and Media Museum Bradford. Photographs of the Rotacolor Prints by Josephine Diecke, SNSF project Film Colors. Technologies, Cultures, Institutions and Joëlle Kost, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors.
Rota Farbenfilm Samples (Kodak Film Samples Collection). Credit: National Science and Media Museum Bradford. Photographs of the Rotacolor Prints by Josephine Diecke, SNSF project Film Colors. Technologies, Cultures, Institutions and Joëlle Kost, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors.
13 Images in 2 Galleries
-
![]() Screenshot from Mayorov, Nikolai (2012): Soviet Colours. Translated by Birgit Beumers. In: Studies in Russian & Soviet Cinema, 6:2, pp. 241–255. doi: 10.1386/srsc.6.2.241_1 Courtesy of Nikolai Mayorov.
Screenshot from Mayorov, Nikolai (2012): Soviet Colours. Translated by Birgit Beumers. In: Studies in Russian & Soviet Cinema, 6:2, pp. 241–255. doi: 10.1386/srsc.6.2.241_1 Courtesy of Nikolai Mayorov.
1 Image
-
![]() Source: Coe, Brian (1981): The History of Movie Photography. Westfield, N.J.: Eastview Editions. Film: Pagliacci (1937).
Source: Coe, Brian (1981): The History of Movie Photography. Westfield, N.J.: Eastview Editions. Film: Pagliacci (1937).
9 Images in 2 Galleries
-
![]() Color reconstruction. Credit: Gisela Harich-Hamburger, Diplomrestauratorin (FH).
Color reconstruction. Credit: Gisela Harich-Hamburger, Diplomrestauratorin (FH).
- Source: Heymer, Gerd (1933): Auflösungsvermögen und Farbwiedergabe in der Farbrasterphotographie. In: Veröffentlichungen des wissenschaftlichen Zentral-Laboratoriums der photographischen Abteilung Agfa, 3, 1933, pp. 188-207.
- Source: Weil, F. (1933): The Optical-Photographic Principles of the Agfacolor Process. In: Journal of the Society of Motion Picture Engineers, 20, (April, 1933), No. 4, p. 301-308.
- Both the Kodak and Agfa lenticular processes required the correct banded filter to be used with each different batch of panchromatic film. These two filters were for different batches of Agfacolor used in a Leica camera.. Source: Coote, Jack H. (1993): The Illustrated History of Colour Photography. Surbiton, Surrey: Fountain Press.
- Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Ede, François (1994): Jour de fête ou la couleur retrouvée. Cahiers du Cinéma: Paris.
- Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
- Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
- Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
- Magnification 5x, front. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Magnification 10x, back. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Magnification 20x, front. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Reflection on Agfacolor lenticular film. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. In: Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Reconstruction of lenticular film by Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland in the framework of their research project doLCE
- Agfacolor Lenticular sample from the Kodak Film Samples Collection at the National Science and Media Museum in Bradford. Credit: National Science and Media Museum Bradford. Photographs by Barbara Flueckiger in collaboration with Noemi Daugaard.
- Analog reconstruction by Giorgio Trumpy, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors
15 Images
-
![]() Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
- Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
2 Images
-
![]() Credit: Harvard Film Archive, George Huizinga Collection, item no. 10454. Film: Prehistoric Women (1951).
Credit: Harvard Film Archive, George Huizinga Collection, item no. 10454. Film: Prehistoric Women (1951).
- Credit: Harvard Film Archive, George Huizinga Collection, item no. 10454. Film: Prehistoric Women (1951).
- Source: Coe, Brian (1981): The History of Movie Photography. Westfield, N.J.: Eastview Editions.
- Reflection on Cinecolor print. Credit: Image courtesy of the 20th Century Fox Collection at the Academy Film Archive. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger
- Reflection on Cinecolor 16 mm print. Credit: Library of Congress. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger
93 Images in 9 Galleries
-
![]() Credit: Image courtesy of the Academy Film Archive. Film: Gone with the Wind (USA 1939, Victor Fleming). Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
Credit: Image courtesy of the Academy Film Archive. Film: Gone with the Wind (USA 1939, Victor Fleming). Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Film: Samson and Delilah (US 1949, Cecil B. DeMille), trailer.
- Photomicrograph, 50x. Credit: Norbert Wey, Institute of Pathology, University of Zurich.
- Photomicrograph, 100x. Credit: Norbert Wey, Institute of Pathology, University of Zurich.
1881 Images in 65 Galleries
Dufaycolor was a regular line screen process whereby the incident light was filtered through a pattern of tiny color patches created by lines in red, green and blue, the so called réseau.
-
![]() Reversal Colour Positive. Credit: Courtesy of BFI National Archive. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger. Film: A Colour Box (GB 1935, Len Lye).
Reversal Colour Positive. Credit: Courtesy of BFI National Archive. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger. Film: A Colour Box (GB 1935, Len Lye).
- Microscopic image of the filter structure of a Dufaycolor film. The Emulsion has been removed. The visible structures are not silver grain but the structure of the filter layers. Credit: David Pfluger, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors. Imaging was performed with support of the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.
- Microscopic images of Dufaycolor film with the focus set at different points within the emulsion and filter layers. The images have been chained to show a travelling through the 3-dimensional structure of the layers. Credit: David Pfluger, conversion to video by Martin Weiss, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors. Imaging was performed with support of the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.
231 Images in 9 Galleries
-
![]() Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
- Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
- Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
3 Images
-
![]() Source: Dubray, J.A. (1933): The Morgana Process In: Journal of the Society of Motion Picture Engineers 21,5, 1933, pp. 403-412.
Source: Dubray, J.A. (1933): The Morgana Process In: Journal of the Society of Motion Picture Engineers 21,5, 1933, pp. 403-412.
1 Image
Gasparcolor was the first three-color multi-layer monopack film available for practical use. It was a double-coated print film with a cyan layer on one side and two layers dyed magenta and yellow on the other side (see illustrations).
-
![]() Uit het rijk der kristallen (NDL 1927?, J.C. Mol). Credit: EYE Film Museum. Photographs of the Dufaycolor and Gasparcolor nitrate print by Barbara Flueckiger.
Uit het rijk der kristallen (NDL 1927?, J.C. Mol). Credit: EYE Film Museum. Photographs of the Dufaycolor and Gasparcolor nitrate print by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Kreise (English title Circles) (Oskar Fischinger, GER 1933-34) Oskar Fischinger's own nitrate print. Credit: Library of Congress, (c) Fischinger Trust, courtesy Center for Visual Music. Photograph Fischinger's own nitrate print by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Credit: (c) Fischinger Trust, courtesy Center for Visual Music. Film: Allegretto by Oskar Fischinger (1936-1943).
- Credit: (c) Fischinger Trust, courtesy Center for Visual Music. Film: Gasparcolor tests by Oskar Fischinger, c. 1933-34.
- Credit: Cinémathèque suisse. Film: Komposition in Blau (Composition in Blue) AKA Lichtkonzert Nr. 1 (Light-Concert No. 1) (GER 1935, Oskar Fischinger).
- Credit: Cinémathèque suisse. © Fischinger Trust, courtesy Center for Visual Music. Film: Komposition in Blau (Composition in Blue) AKA Lichtkonzert Nr. 1 (Light-Concert No. 1) (GER 1935, Oskar Fischinger).
- Credit: Cinémathèque suisse. © Fischinger Trust, courtesy Center for Visual Music. Film: Komposition in Blau (Composition in Blue) AKA Lichtkonzert Nr. 1 (Light-Concert No. 1) (GER 1935, Oskar Fischinger).
- Source: Coe, Brian (1981): The History of Movie Photography. Westfield, N.J.: Eastview Editions.
- Color chart on Agfa Tripofilm. This was the raw stock used for Gasparcolor in Germany until about 1939. Source: Arens, Hans; Heymer, Gerd (1939): Die „Agfa-Farbentafel für Farbenphotographie“. In: Veröffentlichungen des wissenschaftlichen Zentral-Laboratoriums der photographischen Abteilung Agfa, Vol. 6, 1939, pp. 225-229. Leipzig: Hirzel. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 213.
398 Images in 24 Galleries
-
![]() Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Magic Isle.
40 Images
-
![]() Projection of lenticular film in Bocca-Rudatis. Refraction of light beams through lens. Source: Pierotti, Federico (2016): Un'archeologia del colore nel cinema italiano. Dal Technicolor ad Antonioni. Pisa: Edizioni ETS, p. 81.
Projection of lenticular film in Bocca-Rudatis. Refraction of light beams through lens. Source: Pierotti, Federico (2016): Un'archeologia del colore nel cinema italiano. Dal Technicolor ad Antonioni. Pisa: Edizioni ETS, p. 81.
1 Image
-
![]() Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. A History of Motion Picture Color Technology.
Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. A History of Motion Picture Color Technology.
- Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
2 Images
-
![]() Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
- Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
- Source: Kistler, L. R. (1945): The Projection of Thomascolor Motion Pictures. In: International Projectionist, 20,7, Jul., pp. 12–14.
- Source: Kistler, L. R. (1945): The Projection of Thomascolor Motion Pictures. In: International Projectionist, 20,7, Jul., pp. 12–14.
- Left: Thomascolor camera lens mount for converting standard motion picture camera into Thomascolor. Right: A closeup of the Thomascolor projector lens mount for standard film projectors. The inventor points out that this is all that is needed to convert a standard projector to Thomascolor. Source: Anonymous (1944): Thomascolor. Four-Color Process For Motion Pictures. In: International Projectionist, 19,10, Oct., pp. 7–9.
5 Images
-
![]() Cross-section of the optical system displaying the different lenses, the prism and the four filters. Source: Pierotti, Federico (2016): Un'archeologia del colore nel cinema italiano. Dal Technicolor ad Antonioni. Pisa: Edizioni ETS, p. 71.
Cross-section of the optical system displaying the different lenses, the prism and the four filters. Source: Pierotti, Federico (2016): Un'archeologia del colore nel cinema italiano. Dal Technicolor ad Antonioni. Pisa: Edizioni ETS, p. 71.
- 35mm black and white film strip with four equal-sized images (left) and 16mm projector with Cristiani-Mascarini optical system. Source: Pierotti, Federico (2016): Un'archeologia del colore nel cinema italiano. Dal Technicolor ad Antonioni. Pisa: Edizioni ETS, p. 71.
2 Images
-
![]() Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
- Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
2 Images
-
![]() Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
- Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
- Source: Coe, Brian (1981): The History of Movie Photography. Westfield, N.J.: Eastview Editions.
- Schmidt, Richard / Kochs, Adolf (1943): Farbfilmtechnik. Eine Einführung für Filmschaffende. Berlin: Hesse, pp. 54-72. (Schriftenreihe der Reichsfilmkammer, 10.) (in German) [quote id='5']
- Schmidt, Richard / Kochs, Adolf (1943): Farbfilmtechnik. Eine Einführung für Filmschaffende. Berlin: Hesse, pp. 54-72. (Schriftenreihe der Reichsfilmkammer, 10.) (in German) [quote id='5']
9 Images in 1 Gallery
“In 1930 Mannes and Godowsky were invited to join the staff of the Kodak Research Laboratory, where they concentrated on methods of processing multilayer films, while their colleagues worked out ways of manufacturing them. The result was the new Kodachrome film, launched in 1935. Three very thin emulsion layers were coated on film base, the emulsions being sensitised with non-wandering dyes to red, green and blue light, the red-sensitive layer being at the bottom.” (Coe, Brian (1978): Colour Photography. The First Hundred Years 1840-1940. London: Ash & Grant, pp. 121 ff.)
-
![]() Credit: Lichtspiel / Kinemathek Bern. Film: New York, Taufe und Ausflug (CH 1954, Donald Brun).
Credit: Lichtspiel / Kinemathek Bern. Film: New York, Taufe und Ausflug (CH 1954, Donald Brun).
- Surface emulsion side, raking light. Credit: Carsta Knaack, HTW Berlin. Film: Regular 8mm home movie, anonymous 1975.
92 Images in 6 Galleries
-
![]() Münchhausen (Josef von Báky, Germany 1943). Credit: Bundesarchiv Filmarchiv and Friedrich-Wilhelm-Murnau-Stiftung. Photographs of the Agfacolor safety print (acetate) by Barbara Flueckiger.
Münchhausen (Josef von Báky, Germany 1943). Credit: Bundesarchiv Filmarchiv and Friedrich-Wilhelm-Murnau-Stiftung. Photographs of the Agfacolor safety print (acetate) by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Opfergang (GER 1944, Veit Harlan), magnification. Credit: Print from the Filmmuseum Düsseldorf. © Friedrich Wilhelm Murnau Foundation, Wiesbaden. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Paper print. Source: Serda, Charlott (1941): Das Farbfoto-Buch vom Film. Breitkopf & Härtel: Leipzig.
- Parade (1960). Credit: Harvard Film Archive, Brandon Film Library Collection, item no. 14303. Photographs of Agfacolor negative on Orwocolor reversal print by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Parade (1960). Credit: Harvard Film Archive, Brandon Film Library Collection, item no. 14303. Photographs of Agfacolor negative on Orwocolor reversal print by Barbara Flueckiger.
640 Images in 21 Galleries
-
![]() Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: Captain Calamity (1936)
Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: Captain Calamity (1936)
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: Captain Calamity (1936)
2 Images
-
![]() Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
- Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
- Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
- Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Ede, François (1994): Jour de fête ou la couleur retrouvée. Cahiers du Cinéma: Paris.
- Schmidt, Richard / Kochs, Adolf (1943): Farbfilmtechnik. Eine Einführung für Filmschaffende. Berlin: Hesse, pp. 54-72. (Schriftenreihe der Reichsfilmkammer, 10.) (in German) [quote id='6']
5 Images
-
![]() Zaveshchanie/The Testament (7 June 1937). Credit: Courtesy of Nikolai Mayorov.
Zaveshchanie/The Testament (7 June 1937). Credit: Courtesy of Nikolai Mayorov.
- Zaveshchanie/The Testament (7 June 1937). Credit: Courtesy of Nikolai Mayorov. Credit: Courtesy of Nikolai Mayorov.
- The Miraculous Traffic Light (1938). Credit: courtesy of Nikolai Mayorov
- The Wolf and Seven Goat-Kids (1938). Credit: Courtesy of Nikolai Mayorov.
- The Fox and the Wolf (1937). Credit: Courtesy of Nikolai Mayorov.
- The Fox and the Wolf (1937). Credit: Courtesy of Nikolai Mayorov.
6 Images
-
![]() Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
1 Image
-
![]() Agfa Pantachrom. Source: Arens, Hans; Heymer, Gerd (1939): Die „Agfa-Farbentafel für Farbenphotographie“. In: Veröffentlichungen des wissenschaftlichen Zentral-Laboratoriums der photographischen Abteilung Agfa, Vol. 6, 1939, pp. 225-229. Leipzig: Hirzel. Photograph by Martin Weiss, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors.
Agfa Pantachrom. Source: Arens, Hans; Heymer, Gerd (1939): Die „Agfa-Farbentafel für Farbenphotographie“. In: Veröffentlichungen des wissenschaftlichen Zentral-Laboratoriums der photographischen Abteilung Agfa, Vol. 6, 1939, pp. 225-229. Leipzig: Hirzel. Photograph by Martin Weiss, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors.
19 Images in 3 Galleries
-
![]() Agfacolor B original negative. Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Jan Roháč z Dubé (Czechoslovakia 1947, Vladimír Borsky).
Agfacolor B original negative. Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Jan Roháč z Dubé (Czechoslovakia 1947, Vladimír Borsky).
- Faded Agfacolor period nitrate print. Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Jan Roháč z Dubé (Czechoslovakia 1947, Vladimír Borský).
- Agfacolor B original negative. Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Jan Roháč z Dubé (Czechoslovakia 1947, Vladimír Borsky).
- Faded Agfacolor period nitrate print. Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Jan Roháč z Dubé (Czechoslovakia 1947, Vladimír Borský).
- Agfacolor B original negative. Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Jan Roháč z Dubé (Czechoslovakia 1947, Vladimír Borsky).
- Agfacolor B original negative. Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Kvítí z Čech (Czechoslovakia 1947, dir. Václav Jan Staněk).
- Agfacolor positive nitrate print. Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Kvítí z Čech (Czechoslovakia 1947, dir. Václav Jan Staněk).
- Agfacolor positive nitrate print. Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Kvítí z Čech (Czechoslovakia 1947, dir. Václav Jan Staněk).
- Agfacolor B original negative. Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Mistr třeboňský (Czechoslovakia 1950, dir. František Kudláč).
- Agfacolor B original negative. Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Mistr třeboňský (Czechoslovakia 1950, dir. František Kudláč).
- Agfacolor positive nitrate print. Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Mistr třeboňský (Czechoslovakia 1950, dir. František Kudláč).
- Agfacolor B original negative. Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Praha v říjnu (Czechoslovakia 1945, dir. František Sádek).
- Faded Agfacolor period nitrate print. Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Praha v říjnu (Czechoslovakia 1945, dir. František Sádek).
- Agfacolor B original negative. Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Praha v říjnu (Czechoslovakia 1945, dir. František Sádek).
- Agfacolor B original negative. Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Zasadil dědek řepu (Czechoslovakia 1945, dir. Jiří Trnka).
- Agfacolor positive nitrate print. Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Zasadil dědek řepu (Czechoslovakia 1945, Jiří Trnka).
- Agfacolor positive nitrate print. Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Zasadil dědek řepu (Czechoslovakia 1945, Jiří Trnka).
- Credit: By courtesy of Deutsche Kinemathek, Berlin. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger. Film: 1/50 Sekunde, commercial for Niggemeyer Foto/Kino (1952).
- Schmidt, Richard / Kochs, Adolf (1943): Farbfilmtechnik. Eine Einführung für Filmschaffende. Berlin: Hesse, pp. 77-98. (Schriftenreihe der Reichsfilmkammer, 10.) (in German) [quote cite='35875']
- Schmidt, Richard / Kochs, Adolf (1943): Farbfilmtechnik. Eine Einführung für Filmschaffende. Berlin: Hesse, pp. 77-98. (Schriftenreihe der Reichsfilmkammer, 10.) (in German) [quote cite='35875']
- Schmidt, Richard / Kochs, Adolf (1943): Farbfilmtechnik. Eine Einführung für Filmschaffende. Berlin: Hesse, pp. 77-98. (Schriftenreihe der Reichsfilmkammer, 10.) (in German) [quote cite='35875']
21 Images
Agfacolor Negative type G was a chromogenic camera negative balanced for Tungsten illumination.
-
![]() Original Agfacolor negative G. Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Neposlušný zajíček (German title Klein, aber Oho!, Horst von Möllendorff, Czechoslovakia 1944).
Original Agfacolor negative G. Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Neposlušný zajíček (German title Klein, aber Oho!, Horst von Möllendorff, Czechoslovakia 1944).
- Schmidt, Richard / Kochs, Adolf (1943): Farbfilmtechnik. Eine Einführung für Filmschaffende. Berlin: Hesse, pp. 77-98. (Schriftenreihe der Reichsfilmkammer, 10.) (in German) [quote cite='35875']
- Schmidt, Richard / Kochs, Adolf (1943): Farbfilmtechnik. Eine Einführung für Filmschaffende. Berlin: Hesse, pp. 77-98. (Schriftenreihe der Reichsfilmkammer, 10.) (in German) [quote cite='35875']
14 Images in 2 Galleries
-
![]() Agfacolor B negative on Agfacolor positive. Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Tábor (Oldřich Mirad, Czechoslovakia 1953). Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
Agfacolor B negative on Agfacolor positive. Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Tábor (Oldřich Mirad, Czechoslovakia 1953). Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
37 Images in 2 Galleries
-
![]() Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 167.
Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 167.
- Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 166.
2 Images
-
![]() Skleněné varhany (Stěklanna je garmonika, Andrej Chržanovskij, USSR 1968). Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger
Skleněné varhany (Stěklanna je garmonika, Andrej Chržanovskij, USSR 1968). Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger
15 Images in 3 Galleries
-
![]() Source: Cornwell-Clyne, Adrian (1951): Colour Cinematography. London: Chapman & Hall.
Source: Cornwell-Clyne, Adrian (1951): Colour Cinematography. London: Chapman & Hall.
- Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Cornwell-Clyne, Adrian (1951): Colour Cinematography. London: Chapman & Hall.
- Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Cornwell-Clyne, Adrian (1951): Colour Cinematography. London: Chapman & Hall.
- Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Cornwell-Clyne, Adrian (1951): Colour Cinematography. London: Chapman & Hall.
- Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Cornwell-Clyne, Adrian (1951): Colour Cinematography. London: Chapman & Hall.
- Coote, Jack (1948): New Three-Color Camera, In: Journal of the Society of Motion Picture Engineers, vol. 50, June 1948, pp. 543-553.
- Coote, Jack (1948): New Three-Color Camera, In: Journal of the Society of Motion Picture Engineers, vol. 50, June 1948, pp. 543-553.
19 Images in 3 Galleries
“The Konicolor system, introduced by Konishiroku Shashin Kogyo (Now Konica Minolta Holdings, Inc.), split the image into three colors and shot them separately onto three b&w films. In that sense it had something in common with the US ‘Technicolor system’, but this was not a contact print with color dye to create positive film, but used coated emulsion to develop each color in a triple process, which is peculiar. […].”
-
![]() Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris. Film: Test for Jour de Fête.
Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris. Film: Test for Jour de Fête.
- Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
- Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
3 Images
-
![]() Rouxcolor, four-color, black and white negative and positive, ca. 1948. Credit: Gert Koshofer Collection. Sample No. 83. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger
Rouxcolor, four-color, black and white negative and positive, ca. 1948. Credit: Gert Koshofer Collection. Sample No. 83. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger
- Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
7 Images in 1 Gallery
-
![]() Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Cornwell-Clyne, Adrian (1951): Colour Cinematography. London: Chapman & Hall.
Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Cornwell-Clyne, Adrian (1951): Colour Cinematography. London: Chapman & Hall.
- Source: Cornwell-Clyne, Adrian (1951): Colour Cinematography. London: Chapman & Hall.
2 Images
-
![]() Technichrome, three-color print of bi-pack negatives, 1948. Credit: Gert Koshofer Collection. Sample No. 89. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger
Technichrome, three-color print of bi-pack negatives, 1948. Credit: Gert Koshofer Collection. Sample No. 89. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger
4 Images in 1 Gallery
-
![]() Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
- Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
2 Images
-
![]() Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
- Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
- Source: Sease, V. B. (1949): DuPont's New Color Film. In:American Cinematographer, 30: 240, 257-258.
- Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Sease, V. B. (1949): DuPont's New Color Film. In:American Cinematographer, 30: 240, 257-258.
8 Images in 1 Gallery
-
![]() Faded Ferraniacolor positive from Eastmancolor negative, anamorphic (1:2,35). Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Smrt v sedle (Jindřich Polák, Czechoslovakia 1958).
Faded Ferraniacolor positive from Eastmancolor negative, anamorphic (1:2,35). Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Smrt v sedle (Jindřich Polák, Czechoslovakia 1958).
- Faded Ferraniacolor positive from Eastmancolor negative, anamorphic (1:2,35). Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Smrt v sedle (Jindřich Polák, Czechoslovakia 1958).
- Faded Ferraniacolor positive from Eastmancolor negative, anamorphic (1:2,35). Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Smrt v sedle (Jindřich Polák, Czechoslovakia 1958).
- Faded Ferraniacolor positive from Eastmancolor negative, anamorphic (1:2,35). Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Smrt v sedle (Jindřich Polák, Czechoslovakia 1958).
- Faded Ferraniacolor positive from Eastmancolor negative, anamorphic (1:2,35). Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Smrt v sedle (Jindřich Polák, Czechoslovakia 1958).
- Faded Ferraniacolor positive from Eastmancolor negative, anamorphic (1:2,35). Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Smrt v sedle (Jindřich Polák, Czechoslovakia 1958).
- Faded Ferraniacolor positive from Eastmancolor negative, anamorphic (1:2,35). Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Smrt v sedle (Jindřich Polák, Czechoslovakia 1958).
217 Images in 8 Galleries
-
![]() Don't Look Now (GBR / ITA 1973, Nicolas Roeg). Credit: BFI National Film Archive. Photographs of the faded Fujicolor HP Positive Film Type 8813 by Joëlle Kost, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors.
Don't Look Now (GBR / ITA 1973, Nicolas Roeg). Credit: BFI National Film Archive. Photographs of the faded Fujicolor HP Positive Film Type 8813 by Joëlle Kost, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors.
141 Images in 7 Galleries
-
![]() Alien (USA 1979, Ridley Scott). Credit: Library of Congress. Photographs of the Eastman Color Print Film from 1979 by Joëlle Kost, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors.
Alien (USA 1979, Ridley Scott). Credit: Library of Congress. Photographs of the Eastman Color Print Film from 1979 by Joëlle Kost, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors.
- Photomicrograph of modern chromogenic stock, . Credit: Silvana Konermann.
- Eastman Color chromogenic monopack. Source: Craig, G.J. (1953): Eastman Colour Films for Professional Motion Picture Work. In: British Kinematography, 22,5, 1953, pp. 146-158.
- Color fading of Eastmancolor stock. Credit: Collection Gert Koshofer, Bergisch Gladbach (Germany). Source: Schultze, Werner (1953): Farbenphotographie und Farbenfilm. Wissenschaftliche Grundlagen und technische Gestaltung. Berlin: Springer.
- Color reconstruction by Rudolf Gschwind, University of Basel. Credit: Collection Gert Koshofer, Bergisch Gladbach (Germany).
- Color fading of Eastmancolor stock.
- Source: Schultze, Werner (1953): Farbenphotographie und Farbenfilm. Wissenschaftliche Grundlagen und technische Gestaltung. Berlin/Göttingen /Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag. Photograph by Martin Weiss, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors.
- Source: Schultze, Werner (1953): Farbenphotographie und Farbenfilm. Wissenschaftliche Grundlagen und technische Gestaltung. Berlin/Göttingen /Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag. Photograph by Martin Weiss, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors.
707 Images in 23 Galleries
-
![]() Ansco Color, positives of Ansco Color negative, ca. 1952. Credit: Gert Koshofer Collection. Sample No. 10. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
Ansco Color, positives of Ansco Color negative, ca. 1952. Credit: Gert Koshofer Collection. Sample No. 10. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Source: Schultze, Werner (1953): Farbenphotographie und Farbenfilm. Wissenschaftliche Grundlagen und technische Gestaltung. Berlin/Göttingen /Heidelberg: Springer.
- Source: Schultze, Werner (1953): Farbenphotographie und Farbenfilm. Wissenschaftliche Grundlagen und technische Gestaltung. Berlin/Göttingen /Heidelberg: Springer.
- Source: Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers; ed. (1957): The Elements of Color in Professional Motion Pictures. Prepared by a special committee of the Society. Wilton R. Holm, chairman. New York: The Society.
- Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
- Source: Schultze, Werner (1953): Farbenphotographie und Farbenfilm. Wissenschaftliche Grundlagen und technische Gestaltung. Berlin/Göttingen /Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag. Photograph by Martin Weiss, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors.
- Source: Schultze, Werner (1953): Farbenphotographie und Farbenfilm. Wissenschaftliche Grundlagen und technische Gestaltung. Berlin/Göttingen /Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag. Photograph by Martin Weiss, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors.
30 Images in 2 Galleries
-
![]() Credit: By courtesy of Deutsche Kinemathek, Berlin. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger. Film: Commercial Denkt rechtzeitig daran (GER 1952).
Credit: By courtesy of Deutsche Kinemathek, Berlin. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger. Film: Commercial Denkt rechtzeitig daran (GER 1952).
- Credit: By courtesy of Deutsche Kinemathek, Berlin. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger. Film: 1/50 Sekunde, commercial for Niggemeyer Foto/Kino (1952).
13 Images in 2 Galleries
-
![]() Cross section scheme of Eastman Color Type 5248. Scource: Hanson, W. T., Jr.; Kisner, W. I. (1953): Improved Color Films for Color Motion-Picture Production. In: Journal SMPTE, Vol. 61, Dec. 1953, p. 699.
Cross section scheme of Eastman Color Type 5248. Scource: Hanson, W. T., Jr.; Kisner, W. I. (1953): Improved Color Films for Color Motion-Picture Production. In: Journal SMPTE, Vol. 61, Dec. 1953, p. 699.
1 Image
-
![]() Negative. Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Princezna se zlatou hvězdou (Martin Frič, Czechoslovakia 1959).
Negative. Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Princezna se zlatou hvězdou (Martin Frič, Czechoslovakia 1959).
- Negative. Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Princezna se zlatou hvězdou (Martin Frič, Czechoslovakia 1959).
- Negative. Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Princezna se zlatou hvězdou (Martin Frič, Czechoslovakia 1959).
- Negative. Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Princezna se zlatou hvězdou (Martin Frič, Czechoslovakia 1959).
- Princezna se zlatou hvězdou (CZE 1959, Martin Frič). Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Photographs of the Agfacolor B negative on Orwocolor positive by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Princezna se zlatou hvězdou (CZE 1959, Martin Frič). Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Photographs of the Agfacolor B negative on Orwocolor positive by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Princezna se zlatou hvězdou (CZE 1959, Martin Frič). Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Photographs of the Agfacolor B negative on Orwocolor positive by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Princezna se zlatou hvězdou (CZE 1959, Martin Frič). Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Photographs of the Agfacolor B negative on Orwocolor positive by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Princezna se zlatou hvězdou (CZE 1959, Martin Frič). Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Photographs of the Agfacolor B negative on Orwocolor positive by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Princezna se zlatou hvězdou (CZE 1959, Martin Frič). Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Photographs of the Agfacolor B negative on Orwocolor positive by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Princezna se zlatou hvězdou (CZE 1959, Martin Frič). Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Photographs of the Agfacolor B negative on Orwocolor positive by Barbara Flueckiger.
11 Images
-
![]() Written on the Wind (1956). Credit: Harvard Film Archive, item no. 3663. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
Written on the Wind (1956). Credit: Harvard Film Archive, item no. 3663. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Credit: Harvard Film Archive, item no. 1781. Film: Le Ballon rouge (1956). Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Credit: Harvard Film Archive, item no. 1781. Film: Le Ballon rouge (1956). Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Surface emulsion side, raking light (tungsten). Credit: Carsta Knaack, HTW Berlin. Film: Robin Hood, 1973.
- Photomicrograph 16x, raking light. Credit: Carsta Knaack, HTW Berlin. Film: Robin Hood, 1973.
- Photomicrograph, toplight on white background. Credit: Carsta Knaack, HTW Berlin. Film: Robin Hood, 1973.
- Photomicrograph 6,4x, top light on white background: picture and perforation area with spots of dye, yellow edge. Credit: Carsta Knaack, HTW Berlin. Film: Ssssss (1973).
- Photomicrograph 10x, top light on white background: picture and perforation area with spots of dye, yellow edge, yellow dye in frame line. Credit: Carsta Knaack, HTW Berlin. Film: Ssssss (1973).
- Photomicrograph 16x, top light on white background: sound track and perforation area with spots of dye, yellow edge. Credit: Carsta Knaack, HTW Berlin. Film: Ssssss (1973).
- Raking light: surface of picture and perforation area with small spots of dye, yellow edge. Credit: Carsta Knaack, HTW Berlin. Film: Ssssss (1973).
- Surface emulsion side, raking light (tungsten). Credit: Carsta Knaack, HTW Berlin. Film: Robin Hood, 1973.
- Vertigo (USA 1958, Alfred Hitchcock). Credit: Harvard Film Archive, item no. 246. HDR photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
2261 Images in 41 Galleries
-
![]() Cross section scheme, Agfacolor Positive Type 5. Scource: Brune, Wolfgang (1955): Ein neues Agfacolor-Positivmaterial (Agfacolor-Positivfilm Typ 5).
Cross section scheme, Agfacolor Positive Type 5. Scource: Brune, Wolfgang (1955): Ein neues Agfacolor-Positivmaterial (Agfacolor-Positivfilm Typ 5).
1 Image
-
![]() Cross section scheme of Anscochrome. Scource: Forrest; John L. (1955): Processing Anscochrome Motion-Picture Films for Industrial and Scientific Applications. In: Journal SMPTE, Vol. 64, Dec. 1955, p. 679.
Cross section scheme of Anscochrome. Scource: Forrest; John L. (1955): Processing Anscochrome Motion-Picture Films for Industrial and Scientific Applications. In: Journal SMPTE, Vol. 64, Dec. 1955, p. 679.
3 Images in 1 Gallery
-
![]() Recording of a color video signal onto lenticular film.
Recording of a color video signal onto lenticular film.
- Playback of the color image on the lenticular film as a television signal.
2 Images
-
![]() Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Jen počkej X (Nu, pogodi!) (Vjačeslav Kotěnočkin, USSR, 1976).
Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Jen počkej X (Nu, pogodi!) (Vjačeslav Kotěnočkin, USSR, 1976).
- Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Jen počkej X (Nu, pogodi!) (Vjačeslav Kotěnočkin, USSR, 1976).
- Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Jen počkej X (Nu, pogodi!) (Vjačeslav Kotěnočkin, USSR, 1976).
- Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Jen počkej X (Nu, pogodi!) (Vjačeslav Kotěnočkin, USSR, 1976).
- Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Jen počkej X (Nu, pogodi!) (Vjačeslav Kotěnočkin, USSR, 1976).
- Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Jen počkej X (Nu, pogodi!) (Vjačeslav Kotěnočkin, USSR, 1976).
- Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Jak se Žofka postarala o svatbu (Adolf Born, Jaroslav Doubrava, Miloš Macourek, Czechoslovakia 1988).
- Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Jak se Žofka postarala o svatbu (Adolf Born, Jaroslav Doubrava, Miloš Macourek, Czechoslovakia 1988).
- Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Jak se Žofka postarala o svatbu (Adolf Born, Jaroslav Doubrava, Miloš Macourek, Czechoslovakia 1988).
- Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Jak se Žofka postarala o svatbu (Adolf Born, Jaroslav Doubrava, Miloš Macourek, Czechoslovakia 1988).
- Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Jak se Žofka postarala o svatbu (Adolf Born, Jaroslav Doubrava, Miloš Macourek, Czechoslovakia 1988).
- Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Jak se Žofka postarala o svatbu (Adolf Born, Jaroslav Doubrava, Miloš Macourek, Czechoslovakia 1988).
- Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Jak se Žofka postarala o svatbu (Adolf Born, Jaroslav Doubrava, Miloš Macourek, Czechoslovakia 1988).
- Eastmancolor negative on Fomacolor positive. Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Slunečná laguna (Mirko Kačena, Czechoslovakia 1990).
- Eastmancolor negative on Fomacolor positive. Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Slunečná laguna (Mirko Kačena, Czechoslovakia 1990).
- Eastmancolor negative on Fomacolor positive. Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Slunečná laguna (Mirko Kačena, Czechoslovakia 1990).
- Eastmancolor negative on Fomacolor positive. Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Slunečná laguna (Mirko Kačena, Czechoslovakia 1990).
- Eastmancolor negative on Fomacolor positive. Credit: Národní filmový archiv / National Film Archive, Prague. Film: Slunečná laguna (Mirko Kačena, Czechoslovakia 1990).
18 Images
-
![]() Cross section of Ektachrome Commercial, Type 7255. Scource: Groet, N. H./Liberman, M./ Richey, F. (1959): An Improved Professional 16mm Reversal Camera Film. In: JSMPTE, Vol. 68, January 1959, p. 9.
Cross section of Ektachrome Commercial, Type 7255. Scource: Groet, N. H./Liberman, M./ Richey, F. (1959): An Improved Professional 16mm Reversal Camera Film. In: JSMPTE, Vol. 68, January 1959, p. 9.
1 Image
-
![]() Cross section scheme of Eastman Color Negative, Type 5250. Scource: Dundon, Merle L./Zwick, Daan M. (1959): A High Speed Color Negative Film. In: JSMPTE Vol 68, p. 736.
Cross section scheme of Eastman Color Negative, Type 5250. Scource: Dundon, Merle L./Zwick, Daan M. (1959): A High Speed Color Negative Film. In: JSMPTE Vol 68, p. 736.
1 Image
-
![]() cross section scheme of Ektachrome Type 5257 (and 5258). Scource: Groet, N.H./Murray, T.J./Osborne, C.E. (1960): Two High-Speed Color Films and a Reversal Print Film for Motion Picture Use. In: JSMPTE Vol. 69, p. 816.
cross section scheme of Ektachrome Type 5257 (and 5258). Scource: Groet, N.H./Murray, T.J./Osborne, C.E. (1960): Two High-Speed Color Films and a Reversal Print Film for Motion Picture Use. In: JSMPTE Vol. 69, p. 816.
1 Image
-
![]() La perception et l'imaginaire (FRA 1964, Éric Duvivier). Credit: Image'Est. Photographs of the Kodachrome II camera material by Bregt Lameris, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors.
La perception et l'imaginaire (FRA 1964, Éric Duvivier). Credit: Image'Est. Photographs of the Kodachrome II camera material by Bregt Lameris, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors.
- Les autopathes (FRA 1971, Éric Duvivier). Credit: Image'Est. Photographs of the kodachrome reversal by Bregt Lameris, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors.
- Hallucinations: Images du monde visionnaire (FRA 1963, Éric Duvivier). Credit: Image'Est. Photographs of undated Kodachrome II projection print by Bregt Lameris, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors.
84 Images in 5 Galleries
-
![]() Photomicrograph 1000x, Agfachrome cross section. Credit: Carsta Knaack.
Photomicrograph 1000x, Agfachrome cross section. Credit: Carsta Knaack.
- Photomicrograph 500x, Agfachrome cross section. Credit: Carsta Knaack.
2 Images
-
![]() Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 235.
Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 235.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 235.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 235.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 258.
4 Images
-
![]() Frauenschicksale (GDR 1952, Slatan Dudow). Credit: Bundesarchiv Filmarchiv. Photographs of the Orwocolor safety print by Michelle Beutler, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors.
Frauenschicksale (GDR 1952, Slatan Dudow). Credit: Bundesarchiv Filmarchiv. Photographs of the Orwocolor safety print by Michelle Beutler, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors.
- Cross section of Orwo positive print. Credit: Carsta Knaack, HTW Berlin. Film: L'Ours (J.-J. Annaud, 1988).
- Cross section schemes of different materials by Orwo. Source: Kaufmann, Siegfried (1976): Vom ersten Farbumkehrfilm zum Orwochrom-System. In: Bild und Ton, 3/1976, p. 88-93.
1026 Images in 27 Galleries
-
![]() Comparing cross section schemes of different Gevachrome types. Scource: Verbrugghe, R. G. L. (1967): A Sharp Reversal Color Print Film. In: Journal SMPTE, Vol. 76, Dec. 1967, p. 1198.
Comparing cross section schemes of different Gevachrome types. Scource: Verbrugghe, R. G. L. (1967): A Sharp Reversal Color Print Film. In: Journal SMPTE, Vol. 76, Dec. 1967, p. 1198.
10 Images in 1 Gallery
-
![]() NEW!
Soon negative color FOTON daylight films will be available.
FOTONKOLOR NS
roll film 120
FOTONKOLOR NS
roll film 620
FOTONCOLOR NS
roll film 127
FOTONCOLOR NS
35mm (in cartridge)
FOTONCOLOR NS
sheet film
Fotoncolor NS will be possible to expose like 16° DIN, 32 ASA black and white negative film.
NEW!
Soon negative color FOTON daylight films will be available.
FOTONKOLOR NS
roll film 120
FOTONKOLOR NS
roll film 620
FOTONCOLOR NS
roll film 127
FOTONCOLOR NS
35mm (in cartridge)
FOTONCOLOR NS
sheet film
Fotoncolor NS will be possible to expose like 16° DIN, 32 ASA black and white negative film.
1 Image
-
![]() Cross section of Inducolor-print, leader only, title unknown. Credit: Carsta Knaack, HTW Berlin.
Cross section of Inducolor-print, leader only, title unknown. Credit: Carsta Knaack, HTW Berlin.
- Leader of print, title and age unknown. Credit: Carsta Knaack, HTW Berlin.
2 Images
-
![]() Photomicrograph 500x, faded 3M print, cross section. Credit: Karsta Knaack.
Photomicrograph 500x, faded 3M print, cross section. Credit: Karsta Knaack.
- Photomicrograph 500x, faded 3M print, cross section. Credit: Karsta Knaack.
- Faded 3M positive. Credit: Carsta Knaack, HTW Berlin.
- Faded 3M positive. Credit: Carsta Knaack, HTW Berlin.
4 Images
-
![]() Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 218.
Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 218.
1 Image
-
![]() Cross section scheme of different Orwo materials. Source: Kaufmann, Siegfried (1976): Vom ersten Umkehrfilm zum Orwochrom-System. In: Bild und Ton 3/1976, pp. 88-93.
Cross section scheme of different Orwo materials. Source: Kaufmann, Siegfried (1976): Vom ersten Umkehrfilm zum Orwochrom-System. In: Bild und Ton 3/1976, pp. 88-93.
84 Images in 3 Galleries
-
![]() Linear filter structure in Polavision instant Super8 film. The filter lines are running along the film strip. According to the image placement of the Super-8 motion picture standard the image is divided vertically into triplets of R, G and B filter lines. The emulsion layer has been removed before this image was taken.
Credit: David Pfluger, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors. Imaging was performed with support of the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.
Linear filter structure in Polavision instant Super8 film. The filter lines are running along the film strip. According to the image placement of the Super-8 motion picture standard the image is divided vertically into triplets of R, G and B filter lines. The emulsion layer has been removed before this image was taken.
Credit: David Pfluger, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors. Imaging was performed with support of the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.
- Linear filter structure in Polavision instant Super8 film with an emulsion layer of a high photographic density. With the focus set on the emulsion the linear structure of the coloured filters is not visible in this image. Credit: David Pfluger, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors. Imaging was performed with support of the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.
- Comparision of the linear filter structure of Polachrome 35mm instant slide film and Polavision Super-8 motion picture film. While the technical concept behind the two film stocks is the same, the Super-8 film was produced with linear filters of a smaller width. Based on the given width of an RGB filter triplet and the 135 still image size there are about 920 horizontal RGB-triplets per image for a Polachrome slide. The Super-8 film image is rotated by 90° compared to the 135 film still image and has about 340 vertical RGB-triplets per frame. The positioning of the image content compared to the filter lines is indicated in the picture. Credit: David Pfluger, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors. Imaging was performed with support of the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.
- Excerpt of a Polavision Super-8 home movie scanned on a Kinetta scanner in 4.8K resolution edge to edge. In post production a zoom in and out was applied to show the linear filter structure of Polavision film in motion. The zoom was based on image detail from the scan. No upres procedure was applied. Credit: Scanning and editing by Martin Weiss.
- A comparison of the colour filter structures of Dufaycolor, Autochrome and Polavision from Anonymous (1978): Ma il Polavision e' un'altra cosa!. Phototest Italiana, 41, Oct., pp 72–77.
- A comparison of the colour filter structures of Dufaycolor, Autochrome and Polavision from Anonymous (1978): Ma il Polavision e' un'altra cosa!. Phototest Italiana, 41, Oct., pp 72–77. Translation: David Pfluger and Giorgio Trumpy.
- The process of exposure and development of Polavision instant Super-8 film. From Anonymous (1978): Ma il Polavision e' un'altra cosa!. Phototest Italiana, 41, Oct., p. 74.
- The process of exposure and development of Polavision instant Super-8 film. From Anonymous (1978): Ma il Polavision e' un'altra cosa!. Phototest Italiana, 41, Oct., p. 74. Translation: David Pfluger and Giorgio Trumpy.
- "Polavision (top) vs. Kodachrome 40: These are blowups from closely matching frames of Debra Goldie, filmed simultaneously with a Polavision and a conventional super 8 camera, side by side, with the Twi Light quartz lamp mounted on top of the former. Subject distance was 6 ft., but the super 8 camera was focused for 10 ft. – same as the Polavision camera at its close-up setting. Both Polavision and Kodachrome 40 are closely equal in speed, but differ distinctly in structure, faithfulness of color rendition, and latitude, as is obvious from these frame reproductions. What can't be seen is the relative opacity of Polavision: according to our measurement, it transmits less than 9 percent as Kodachrome 40. However, the lab that made the duplicate transparency blow-ups of the frames found that it had to give a full six stops extra exposure." (Leavitt, Don; Drukker Leendert (1978): First Look: Polavision instant movies. In: Popular Photography, Feb., p. 68.)
- "C'est devant un immense agrandissement de l'intérieur d'une cassette Polavision sur la-quelle se découpe la silhouette de l'orateur (ci-contre à gauche) que le Dr Land présenta son invention. Ce document permet de distinguer les poulies de guidage du film (1 et 2), la réserve de produit de traitement et son bec ré-partiteur (3), la bobine débitrice (4), l'ensemble formé par le presseur de film et le prisme (5), la poulie d'entraînement du film (6)." "It was in front of a huge enlargement of the interior of a Polavision cassette on which the silhouette of the speaker was cut out (opposite left) that Dr Land presented his invention. This document makes it possible to distinguish the guide pulleys of the film (1 and 2), the supply of treatment product and its distribution nozzle (3), the supply reel (4), the assembly formed by the presser of film and the prism (5), the film drive pulley (6)." (Anonymous (1977): Naissance du cinéma instantané. In: L'auto-journal, Rubrique realisée sous la direction de Pierre Marais, 12, Jul., pp. 94–95.)
- The production of the Filter structure on Polavision film includes the use of a lenticular surface, which is removed after the process. The lenticules are not involved in recording the color information during the taking of images in the camera. Figure 10 and Figure 11 from: Land, Edwin H. (1997): An Introduction to Polavision. In: Photographic Science and Engineering, 21,5, Sept., Oct., pp. 228–236, on p. 228.
- Comparison of thickness of the image carrying layer in a Kodak fine grain positive and Polavision film. Figure 24 from: Land, Edwin H. (1997): An Introduction to Polavision. In: Photographic Science and Engineering, 21,5, Sept., Oct., pp. 228–236, on p. 235.
- In the Polavision instant color film process the negative image recorded during the exposure of the film is neither developed from a latent image to a visible negative nor is it removed from the film. The latent negative stays as a layer in the film and is responsible for a slight attenuation of the image’s highlights. Figure 25 from: Land, Edwin H. (1997): An Introduction to Polavision. In: Photographic Science and Engineering, 21,5, Sept., Oct., pp. 228–236, on p. 236.
- Single frame of a Polavision home movie scanned in 3.5K resolution.
14 Images
-
![]() Linear filter structure in Polachrome 35mm instant slide film. The blue filter strips are slightly larger compared to the red and green filters. The filter lines are running along the film strip. According to the image placement of the 135 film format for still photography the image is divided horizontally into triplets of R, G and B filter lines.
The emulsion layer has been removed before the image was taken.
Credit: David Pfluger, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors. Imaging was performed with support of the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.
Linear filter structure in Polachrome 35mm instant slide film. The blue filter strips are slightly larger compared to the red and green filters. The filter lines are running along the film strip. According to the image placement of the 135 film format for still photography the image is divided horizontally into triplets of R, G and B filter lines.
The emulsion layer has been removed before the image was taken.
Credit: David Pfluger, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors. Imaging was performed with support of the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.
- Linear filter structure in Polachrome 35mm instant slide film with a emulsion layer of low photographic density. Credit: David Pfluger, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors. Imaging was performed with support of the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.
- Comparision of the linear filter structure of Polachrome 35mm instant slide film and Polavision Super-8 motion picture film. While the technical concept behind the two film stocks is the same, the Super-8 film was produced with linear filters of a smaller width. Based on the given width of an RGB filter triplet and the 135 still image size there are about 920 horizontal RGB-triplets per image for a Polachrome slide. The Super-8 film image is rotated by 90° compared to the 135 film still image and has about 340 vertical RGB-triplets per frame. The positioning of the image content compared to the filter lines is indicated in the picture. Credit: David Pfluger, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors. Imaging was performed with support of the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.
4 Images in 1 Gallery
-
![]() Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 98.
Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 98.
1 Image
-
![]() Source: Jacobson, Egbert (1942): The Color Harmony Manual and How to Use It. Chicago: Color Laboratories Division, Container Corp. of America. Credit: Faber Birren Collection, Yale University. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
Source: Jacobson, Egbert (1942): The Color Harmony Manual and How to Use It. Chicago: Color Laboratories Division, Container Corp. of America. Credit: Faber Birren Collection, Yale University. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
1 Image
-
![]() Didone abbandonata (ITA 1910, Luigi Maggi).
Credit: Cineteca di Bologna.
Photographs of the tinted nitrate print by Barbara Flueckiger.
Didone abbandonata (ITA 1910, Luigi Maggi).
Credit: Cineteca di Bologna.
Photographs of the tinted nitrate print by Barbara Flueckiger.
Frame characteristics / features of margins: Ambrosio. Cf.: Brown, Harold (1990): Physical Characteristics of Early Films as Aids to Identification. Brussels: FIAF, on p. 24.