Select Category▼×
- All Categories
- Bibliography
- Chromogenic monopack
- Chromolytic multilayer
- Color separation
- Double-coated / bi-pack
- Edge Codes and Identification
- Hand coloring
- Other
- Printing / dye-transfer
- Printing / pigment process
- Screen processes
- Spatial synthesis (multiple lenses, beam splitter)
- Stencil coloring (pochoir, Pathécolor)
- Temporal synthesis (rotary filters)
- Theory
- Tinting
- Toning
-
![]() Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
- Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
2 Images
-
![]() Credit: Gert Koshofer Collection. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
Credit: Gert Koshofer Collection. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
- Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
5 Images in 1 Gallery
“The Hérault Trichrome process was demonstrated in Paris on 1 October 1926, with three films made by A. Rodde — a fashion show, a documentary on Brittany and a tableau of the Legend of the King of Ys. Hérault Trichrome was an extension of ...
-
![]() Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress.
Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress.
2 Images
The third Technicolor process used the same camera as process no. II to combine a pair of frames of the red and green record respectively on the b/w negative (see image). In contrast to the former process, however, the two images were printed on one side of the positive by the dye transfer or imbibition process.
-
![]() King of Jazz (USA 1930, John Murray Anderson). Credit: Library of Congress. Photographs of the Technicolor No. III dye-tranfer nitrate print from 1930 and 1931 by Olivia Kristina Stutz, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors.
King of Jazz (USA 1930, John Murray Anderson). Credit: Library of Congress. Photographs of the Technicolor No. III dye-tranfer nitrate print from 1930 and 1931 by Olivia Kristina Stutz, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors.
- Credit: Images courtesy of the Margaret Herrick Library. Film: Corrine Griffith in The Garden of Eden. Photograph: Barbara Flueckiger.
- Credit: George Eastman House Motion Picture Department Collection. Film: Buffalo Bill’s Last Fight (USA 1927, John W. Noble).
- Technicolor ad in Photoplay, 1930. Source: Photoplay, 1930, see Media History Digital Library
- Technicolor ad in Photoplay, 1930. Source: Photoplay, 1930, see Media History Digital Library
- Photomicrograph, 10x. Credit: Silvana Konermann.
- Photomicrograph, 20x. Credit: Silvana Konermann.
- Doctor X (USA 1932, Michael Curtiz). Credit: UCLA Film & Television Archive. Photographs of the Technicolor No. III dye-tranfer nitrate print by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Doctor X (USA 1932, Michael Curtiz). Credit: UCLA Film & Television Archive. Photographs of the Technicolor No. III dye-tranfer nitrate print by Barbara Flueckiger.
1298 Images in 38 Galleries
-
![]() Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 74.
Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 74.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 44.
2 Images
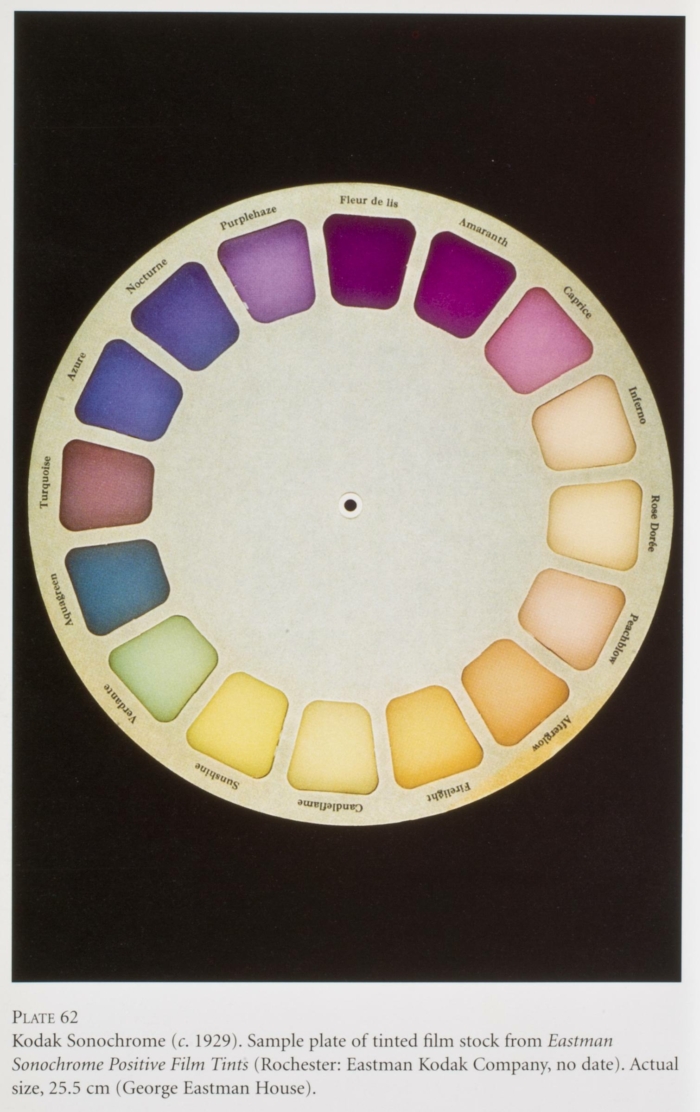
Kodak Sonochrome was a specially prepared tinted film for sound film that did not interfere with the spectral sensitivity of the photo-electric cell for the reading of the optical sound track.
The 17 Sonochrome tints were dyed in mainly light hues ...
-
![]() Credit: Paolo Cherchi Usai. Source: Cherchi Usai, Paolo (2000): Silent Cinema. London: BFI.
Credit: Paolo Cherchi Usai. Source: Cherchi Usai, Paolo (2000): Silent Cinema. London: BFI.
- Source: The International Photographer, July 1929
- Source: The International Photographer, July 1929
- Source: The International Photographer, July 1929
- Source: The International Photographer, July 1929
79 Images in 3 Galleries
“LENTICULAR PROCESS
In 1896 R. E. Liesegang (Ahriman, 1896) suggested a photographic color process based upon the use of banded filters in the camera aperture.
[…]
In 1909 R. Berthon (British Patent 10,611; see also Berthon, 1910a, b) ...
-
![]() Kodacolor lenticular filter for the projector. Lichtspiel / Kinemathek Bern.
Kodacolor lenticular filter for the projector. Lichtspiel / Kinemathek Bern.
- Credit: Rudolf Gschwind, Imaging and Media Lab, University of Basel.
- Magnification of an area. Credit: Rudolf Gschwind, Imaging and Media Lab, University of Basel.
- Color reconstruction test. Credit: Rudolf Gschwind, Imaging and Media Lab, University of Basel.
- Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
- Microscopic linear lens structure of Kodacolor lenticular film. Credit: David Pfluger, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors. Imaging was performed with support of the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.
- Acetate plastic base of Kodacolor lenticular film embedded in epoxide resin. The emulsion layer usually placed on the opposite side of the acetate base has been removed beforehand and is therefore not visible. Credit: David Pfluger, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors. Imaging was performed with support of the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.Credit: David Pfluger, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors. Imaging was performed with support of the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.
- Focal travelling through the 3-dimensional structure of Kodacolor lenticular film. In the beginning the linear lenticular structure is visible and towards the end the emulsion layer comes into focus and the granular structure defined by the density of the silver is visible. In this shot the lenticules were showing towards the light source and the emulsion towards the camera. This enables an undistorted recording of the emulsion layer. Credit: David Pfluger, editing by Martin Weiss, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors. Imaging was performed with support of the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.
- Focal travelling through the 3-dimensional structure of Kodacolor lenticular film. In the beginning the linear lenticular structure is visible and towards the end the emulsion layer comes into focus. In this shot the lenticules were allocated towards the lens of the microscope and the light source at the side of the emulsion similar to the configuration in projection. As a consequence the graininess of the emulsion is not visible as with the film flipped to the other side. The structure is optically distorted perpendicular to the linear structure of the lenticules. Credit: David Pfluger, editing by Martin Weiss, ERC Advanced Grant FilmColors. Imaging was performed with support of the Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis, University of Zurich.
24 Images in 1 Gallery
Several attempts were made to apply the Autochrome process invented by the Lumière brothers to motion pictures.
Transparent potato starch grains with a diameter of 15–20 micrometer were colored in the additive primaries red, green and blue. The ...
-
![]() Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Cinécolor, mosaic screen, ca. 1929. Credit: Gert Koshofer Collection. Sample No. 68. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
- Magnification of an image area. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
27 Images in 2 Galleries
“In the Multicolor (two-color) subtractive process, two negative films are run simultaneously through any standard camera with their emulsion surfaces in contact. The front negative is orthochromatic, with the surface layer dyed orange-red to ...
-
![]() Iridescence on Multicolor print, reflection properties. Credit: Library of Congress. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger
Iridescence on Multicolor print, reflection properties. Credit: Library of Congress. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger
- Magnification 20x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Magnification 10x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Magnification 5x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: Fox Movietone Follies of 1929.
- Source: Coe, Brian (1981): The History of Movie Photography. Westfield, N.J.: Eastview Editions.
- Source: Cornwell-Clyne, Adrian (1951): Colour Cinematography. London: Chapman & Hall.
- Source: Cornwell-Clyne, Adrian (1951): Colour Cinematography. London: Chapman & Hall.
- Credit: Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich. Source: Cornwell-Clyne, Adrian (1951): Colour Cinematography. London: Chapman & Hall.
- Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Magnification of an area. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Reflection properties. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
72 Images in 6 Galleries
-
![]() Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 70.
Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 70.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 70.
- Photomicrograph (20x) of a Finlay screen. Credit: Courtesy of George Eastman House, International Museum of Photography and Film.
- Finlay box. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 39.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 39.
- Source: Pénichon, Sylvie (2013): Twentieth Century Colour Photographs. The Complete Guide to Processes, Identification & Preservation. London, Los Angeles: Thames & Hudson, p. 40.
9 Images in 1 Gallery
-
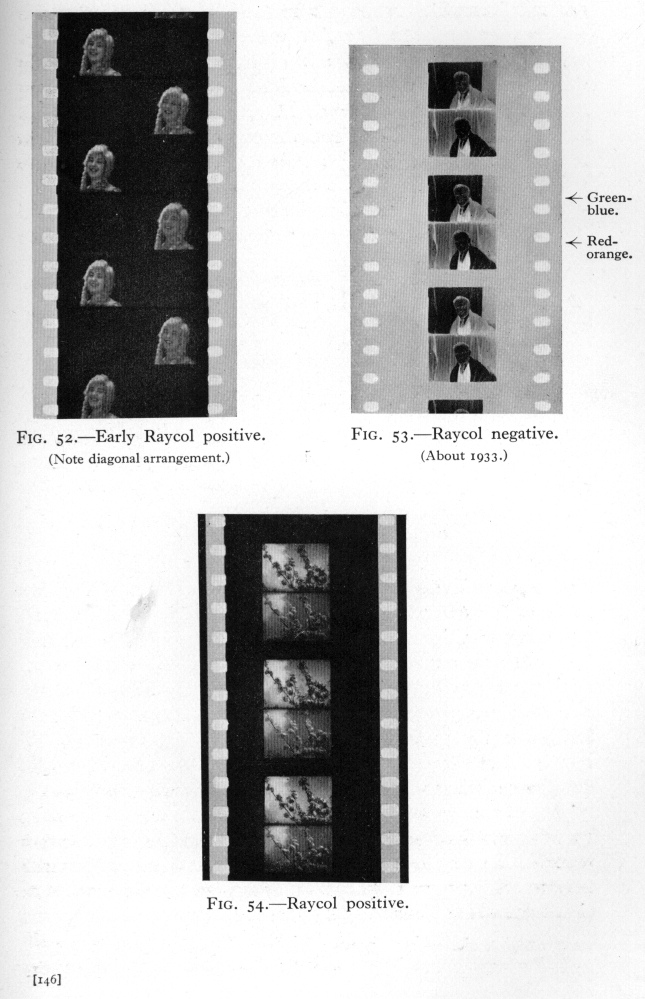
![]() Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
13 Images in 1 Gallery
“The Dutch Sirius Color process (1929) used a camera with a beamsplitting system behind the lens to expose a single film, the film passing through two gates at right angles to each other. The double-coated print film was dye-toned. The process ...
-
![]() Magnification, 20x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
Magnification, 20x. Credit: photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Magnification, 10x. Credit: Photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Magnification, 5x. Credit: Photomicrograph by Silvana Konermann.
- Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. In: Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, Dresden 1931, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Magnification of an image area. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Reflection on the Sirius film, front. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
- Reflection on the Sirius film, back. Source: Eggert, John (1932): Kurzer Überblick über den Stand der Farbenkinematographie. Bericht über den VIII. Internationalen Kongress für wissenschaftliche und angewandte Photographie, pp. 214-222. Leipzig: J. A. Barth.
142 Images in 4 Galleries
“Harriscolor
In this method as in other methods of color photography, independent color value negatives are first obtained. The Harriscolor process can employ one of the following two methods: Either a camera wherein the dividing light prisms ...
-
![]() Credit: Technicolor Collection. George Eastman House Moving Image Department. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
Credit: Technicolor Collection. George Eastman House Moving Image Department. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Credit: Technicolor Collection. George Eastman House Moving Image Department. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
- Credit: Technicolor Collection. George Eastman House Moving Image Department. Photograph by Barbara Flueckiger.
3 Images
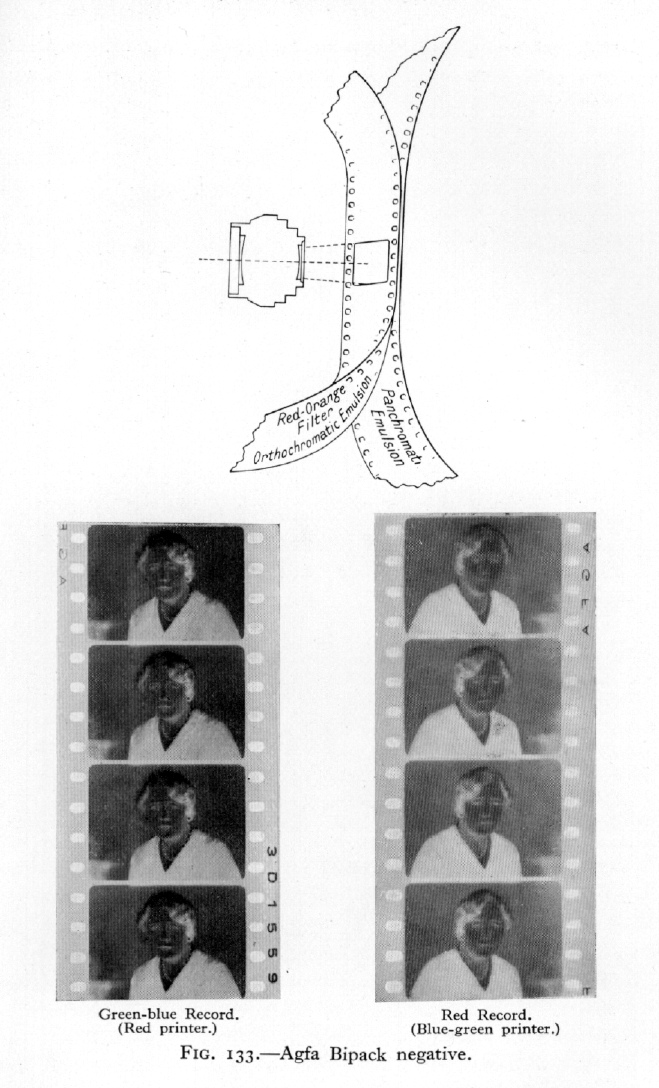
AGFA BIPACK FILM
The front film is orthochromatic and sensitive, therefore, to green and blue. The rear film is panchromatic and records red-orange only, there being a red-orange filter on the orthochromatic emulsion. In fact, this is a bipack of the ...
-
![]() Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
11 Images in 1 Gallery
-
![]() Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
- Source: Klein, Adrian Bernhard (Cornwell-Clyne) (1940): Colour Cinematography. Boston: American Photographic Pub. Co.
- Credit: Cinémathèque française, conservatoire des techniques, Paris.
3 Images
-
![]() Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Gift of Montezuma.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
- Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: The Sweetest Story.
42 Images
“Public showings of the work done at this plant in Hollywood have been given to Los Angeles audiences.
The release prints are made on double sided film. Both sides are developed at one time and then toned red on one side and bluegreen on the ...
-
![]() Strange Birds (US 1930, Mack Sennett). Credit: Library of Congress. Photograph of the nitrate print: Barbara Flueckiger
Strange Birds (US 1930, Mack Sennett). Credit: Library of Congress. Photograph of the nitrate print: Barbara Flueckiger
- Magnification. Credit: Geo. Willeman, Nitrate Film Vault Manager, Library of Congress. Film: Strange Birds (1930)
18 Images in 1 Gallery
-
![]() Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
Principle of capturing and projecting lenticular film. Credit: Joakim Reuteler and Rudolf Gschwind, Digital Humanities Lab, University of Basel, Switzerland. Illustration by Sarah Steinbacher, Multimedia & E-Learning-Services, University of Zurich.
1 Image
“The Brewster Process.
(U.S.P. 1,752,477. 1930-)
Camera. – P. D. Brewster, an American inventor, who was one of the first to apply the bipack system to colour cinematography, has a number of patents to his credit covering various cameras and ...
-
![]() Dyes of Brewster color. Credit: Brian Pritchard.
Dyes of Brewster color. Credit: Brian Pritchard.
- Source: Ryan, Roderick T. (1977): A History of Motion Picture Color Technology. London: Focal Press.
52 Images in 1 Gallery
Unlike other additive systems invented in previous years, Gualtierotti tried to avoid the phenomenon of chromatic aberration inherent in the use of multiple lenses or the creation of successive separation records. The proposed solution was based on ...
-
![]() Rotating filters permitting to adjust tonality and intensity of the colors. Source: Pierotti, Federico (2016): Un'archeologia del colore nel cinema italiano. Dal Technicolor ad Antonioni. Pisa: Edizioni ETS, p. 62
Rotating filters permitting to adjust tonality and intensity of the colors. Source: Pierotti, Federico (2016): Un'archeologia del colore nel cinema italiano. Dal Technicolor ad Antonioni. Pisa: Edizioni ETS, p. 62
1 Image
“An American two-colour subtractive process still worked by the Consolidated Film Industries division of Republic Pictures Corporation. This concern was licensed by the owners of the “Prizma” patents, which it will be remembered was ...
-
![]() Mysore Yesterday and Tomorrow Credit: Image courtesy of the 20th Century Fox Collection at the Academy Film Archive. Photograph: Barbara Flueckiger.
Mysore Yesterday and Tomorrow Credit: Image courtesy of the 20th Century Fox Collection at the Academy Film Archive. Photograph: Barbara Flueckiger.
23 Images in 2 Galleries
“The Rotocolor process was an additive system for color cinematography. The process was announced in 1931 by H. Muller. According to an article in Film Daily, April 12, 1931, and The Motion Picture Herald, April 11, 1931, the process consisted of ...